TECHNOLOGY
Beyond Maps: Unlocking the Power of GPS & GNSS Technology
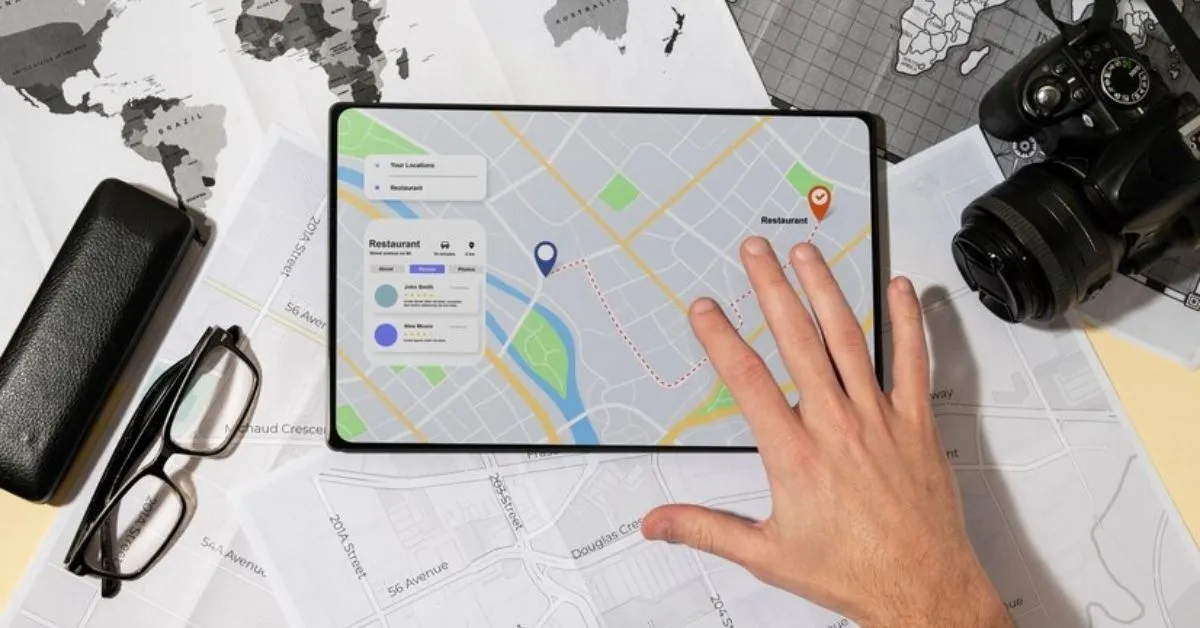
Introduction to GPS and GNSS
In the ever-expanding world of technology, GPS (Global Positioning System) and GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems) are pivotal innovations. Initially developed for military navigation, these systems have transcended their original applications, embedding themselves into the fabric of daily life. Today, they do far more than merely pinpoint locations on a map; they are integral tools in various sectors, including agriculture, aviation, and urban planning, revolutionizing how we interact with our environment.
Understanding GPS and GNSS
The Basics of GPS
GPS is a satellite-based navigation system comprising a satellite network that sends precise signals, allowing receivers on the ground to calculate and display accurate location data. Initially developed by the U.S. Department of Defense, GPS was exclusively for military use during its early development stages. However, it was later opened for civilian use, leading to widespread adoption in countless applications.
The Expansion to GNSS
While GPS is often used interchangeably with GNSS, the latter encompasses a broader spectrum. GNSS includes systems like Russia’s GLONASS, the European Union’s Galileo, and China’s BeiDou. Each system works independently, but in concert, it provides more comprehensive global coverage and increased accuracy through cross-referencing multiple satellites from different systems.
Applications of GPS and GNSS Technology
Navigation and Transportation
The most common use of GPS and GNSS technology remains in navigation. From driving cars on bustling city streets to piloting ships through treacherous waters, these technologies ensure safety and efficiency by providing real-time positional information. Moreover, they are essential for modern logistics, helping to manage and track the movement of goods globally. They also play a critical role in public transportation systems, enhancing route planning and reducing delays by optimising travel paths. Additionally, emergency response teams rely on these accurate location services to reach people in need quickly and effectively, demonstrating their vital importance in critical situations.
Environmental Monitoring and Management
GPS and GNSS technologies are vital tools in environmental conservation and management. They are used for tracking wildlife, monitoring changes in the earth’s surface, and managing natural disasters. By providing accurate data, these systems help scientists and conservationists make informed decisions leading to sustainable practices and policies.
Precision Agriculture
In agriculture, GPS and GNSS technologies have ushered in an era of precision farming. Farmers use these tools to plant seeds at precise locations and efficiently manage tractors and harvesters. This increases crop yields, reduces waste, and minimises environmental impact.
Urban Planning and Development
Urban planners utilise GPS and GNSS data to design more innovative and efficient cities. This includes everything from traffic management to the development of new infrastructure projects. Accurate geospatial data aids in optimally placing buildings, roads, and public transport systems, making cities more livable and reducing congestion.
The Future of GPS and GNSS
Innovations and Improvements
As technology progresses, GPS and GNSS systems continue to evolve. Innovations such as augmented reality (AR) navigation and autonomous vehicle technology rely heavily on improved accuracy and reliability of satellite data. Furthermore, advancements in satellite technology are expected to enhance the precision of these systems, opening up new possibilities for their application.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their vast potential, GPS and GNSS systems face several challenges. Signal interference, both natural and artificial, can disrupt the accuracy of satellite data. Additionally, cybersecurity remains a significant concern, as these systems are crucial for many infrastructures, and their compromise could lead to severe consequences.
Impact on Emerging Markets
Emerging markets stand to gain immensely from adopting GPS and GNSS technologies. In regions like hemisphere Canada, where vast and often remote landscapes dominate, these technologies provide critical support in areas ranging from mining to forestry management, helping to boost local economies and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
GPS and GNSS technologies have evolved far beyond their initial military and navigational uses to become essential elements across various sectors. Their unparalleled ability to provide accurate and reliable location data has made them indispensable in our contemporary world. As technology advances and we continue to innovate and overcome various challenges, the potential for these technologies to further transform our lives and industries is truly boundless. With thoughtful integration, strategic development, and continuous improvement, GPS and GNSS will continue to shape the future of numerous industries, driving significant progress and fostering a better-connected, more efficient, and technologically advanced world. Their technological and socio-economic impact enables better decision-making and efficiency across global platforms.
If you find this article helpful, check out our blog for more informative content.
TECHNOLOGY
adovivo com: Emerging Digital Hub for Modern Online Communities

Getting Started with Adovivo com
Welcome to the digital age, where connections are made with a click and communities thrive beyond geographical boundaries. Enter Adovivo com a vibrant platform that’s redefining how we interact online. Whether you’re looking to build a niche community, share passions, or collaborate on innovative projects, Adovivo com provides all the tools you need in one seamless space. As more individuals seek meaningful interactions in an increasingly virtual world, understanding what sets Adovivo com apart is essential for anyone looking to engage authentically with others. Let’s explore this emerging hub and discover why it could be your next favorite online destination!
Features and Benefits of Adovivo com
Adovivo com stands out with its user-friendly interface. Navigating through the platform feels intuitive, allowing members to connect seamlessly.
One of the key features is customizable community spaces. Users can tailor these spaces to reflect their unique identity and purpose, fostering engagement among members.
Another benefit lies in robust communication tools. Private messaging and group chats enhance interaction, ensuring that discussions remain lively and relevant.
The platform also offers rich multimedia support. Upload images, videos, or share links easily to enrich conversations and keep content dynamic.
Additionally, Adovivo com prioritizes safety with strong moderation options. Community leaders can manage interactions effectively while maintaining a welcoming atmosphere for all participants.
These features collectively create an engaging environment where online communities can thrive effortlessly.
The Rise of Online Communities in Today’s Digital World
Online communities have experienced a remarkable surge in recent years. As technology evolves, people increasingly seek connections beyond physical boundaries.
Social media platforms initially paved the way. They allowed individuals to share ideas and foster relationships with like-minded peers from around the globe. This shift has transformed how we communicate, collaborate, and engage with one another.
Today’s digital landscape embraces diverse groups that cater to various interests and passions. From gaming clans to book clubs, these spaces provide support, knowledge sharing, and a sense of belonging.
As remote work becomes more prevalent, online communities play an essential role in maintaining professional networks as well. They help professionals connect over shared challenges while fostering growth through collaboration.
The appeal lies not just in interaction but also in empowerment. Members can voice opinions freely while finding inspiration from others’ experiences within these vibrant ecosystems.
How Adovivo com Is Different from Other Online Platforms?
Adovivo com stands out in the crowded online platform landscape with its user-centric design. Unlike many competitors, it prioritizes community engagement over mere content sharing.
The interface is intuitive and visually appealing, making navigation seamless for users of all ages. Features like customizable profiles allow individuals to express their unique identities within the community.
What sets Adovivo com apart is its focus on meaningful interactions. The platform fosters genuine connections through interest-based groups, encouraging members to collaborate and share insights.
Moreover, robust moderation tools ensure a safe environment where respectful dialogue flourishes. This commitment to maintaining a positive space enhances member satisfaction significantly.
Adovivo com leverages advanced algorithms to curate personalized content feeds. Users receive tailored suggestions that keep them engaged without overwhelming them with irrelevant information.
Success Stories of Communities on Adovivo com
Adovivo com has become a nurturing ground for diverse online communities, each thriving in its unique way. For instance, a group of aspiring writers found their voice through the platform’s interactive features. They share drafts and receive feedback, fostering creativity and collaboration.
Another success story comes from fitness enthusiasts who formed a supportive community on Adovivo com. Members motivate one another with shared workouts and challenges, turning personal goals into collective achievements.
Even niche hobbyists have carved out spaces within this vibrant ecosystem. A knitting circle blossomed into an international network, exchanging tips and patterns across borders.
These examples showcase how Adovivo com empowers individuals to connect deeply over shared passions. Each community not only flourishes but also enriches the user experience on this dynamic platform.
How to Get Started on Adovivo com?
Getting started on Adovivo com is a straightforward process. First, visit the website and create your account. You’ll need to provide basic information like your name and email.
Once registered, explore different communities that interest you. The platform offers various categories ranging from hobbies to professional networks.
Next, engage with content by liking posts or joining discussions. This engagement allows you to build connections with people who share similar interests.
Don’t hesitate to create your own community if you have a specific niche in mind. Share your vision and invite others who share your passion.
Stay active! Regular participation enhances visibility and fosters meaningful relationships within the community.
The Future of Online Communities and the Role of Adovivo com
The future of online communities is vibrant and full of potential. As digital interactions continue to evolve, platforms like Adovivo com are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping these connections.
Adovivo com champions inclusivity and engagement, making it easier for diverse communities to thrive. With its user-friendly design, members can create meaningful relationships based on shared interests and values.
As more people seek authentic connections, the demand for specialized spaces will rise. Adovivo com recognizes this shift and adapts accordingly, offering tools that empower users to organize events or discussions effortlessly.
Moreover, technological advancements such as AI moderation ensure safe environments while enhancing member experience. This proactive approach sets Adovivo apart from traditional social media networks where noise often drowns out genuine interaction.
In this rapidly changing landscape, Adovivo com stands ready to support the evolution of community dynamics by fostering enriched communication and collaboration across various niches.
Conclusion
Adovivo com is shaping up to be a crucial player in the realm of online communities. As more people seek connection and belonging, platforms like Adovivo offer tailored experiences that foster engagement and growth. With its unique features, user-friendly interface, and focus on community-driven interactions, it stands out as an innovative hub for those looking to connect with others who share their passions.
The rise of digital communication has transformed how we form relationships today. People are continually exploring new avenues for interaction, making places like Adovivo essential for nurturing these connections. The success stories emerging from this platform demonstrate its potential to empower users in ways traditional social networks cannot.
Getting started on Adovivo is simple and intuitive, welcoming individuals from all walks of life to create or join vibrant communities. As the landscape evolves further toward digital connectivity, Adovivo com remains dedicated to enhancing user experiences while facilitating meaningful interactions among members.
As you explore the possibilities within this dynamic platform, consider how your own interests could thrive in such a supportive environment. Embrace the future of online communities where creativity meets collaboration and discover what makes Adovivo com’s a standout choice for anyone seeking authentic connections online.
TECHNOLOGY
Erpoz: The Emerging Idea Shaping Modern Entrepreneurial Strategy

Introduction to Erpoz: What is it?
In the fast-paced world of entrepreneurship, innovation is key. One of the latest concepts making waves in this realm is Erpoz. But what exactly is Erpoz? This emerging idea blends traditional strategies with modern practices, offering entrepreneurs a fresh perspective on how to navigate an ever-changing market landscape. As businesses strive to stay relevant and competitive, understanding Erpoz could be the game-changer you’ve been looking for. Dive in as we explore its origins, core elements, and how it’s reshaping entrepreneurial strategy today. If you’re ready to elevate your business approach, you won’t want to miss this journey into the heart of Erpoz!
The History of Erpoz and Its Evolution in Entrepreneurial Strategy
Erpoz emerged in the early 21st century, born out of a need for agility in business. As markets shifted rapidly, entrepreneurs sought strategies that could adapt quickly to changing landscapes.
Initially focused on technology integration, Erpoz began as a framework for startups. It emphasized lean methodologies and data-driven decision-making. Over time, it evolved to encompass broader aspects of entrepreneurial strategy.
The rise of digital platforms fueled its development further. Entrepreneurs realized they needed more than just tech; they required holistic approaches that included customer engagement and sustainability.
As Erpoz matured, it attracted attention from established corporations looking to innovate their processes. This shift highlighted its relevance across various industries beyond startups.
Today, Erpoz represents a dynamic interplay between tradition and modern practices—guiding entrepreneurs toward resilience and growth amidst uncertainty.
Key Elements of Erpoz
At its core, Erpoz emphasizes adaptability. This principle allows businesses to pivot quickly in response to market changes. Flexibility drives innovation and keeps companies relevant.
Collaboration is another essential element of Erpoz. It fosters teamwork across departments and encourages diverse perspectives. When employees come together, they create more robust solutions.
Data-driven decision-making plays a pivotal role as well. Utilizing analytics helps entrepreneurs understand consumer behavior and market trends better. Relying on data minimizes risks associated with intuition-based decisions.
The focus on sustainability cannot be overlooked. Modern consumers are increasingly eco-conscious, prompting businesses to adopt sustainable practices within their strategies.
These key elements collectively shape an entrepreneurial framework that thrives amidst uncertainty while promoting growth and resilience in today’s competitive landscape.
Examples of Companies Utilizing Erpoz in Their Strategies
Several companies are embracing erpoz to reshape their business models. One standout example is a tech startup that integrates AI with customer feedback loops. By doing so, they tailor their products in real-time based on user preferences.
Another notable case is an e-commerce platform utilizing erpoz for enhanced supply chain efficiency. They leverage data analytics to predict consumer demand, ensuring optimal inventory levels and reducing waste.
In the hospitality sector, a boutique hotel chain applies erpoz principles by personalizing guest experiences through smart technology. From room preferences to personalized recommendations, every touchpoint is crafted around individual needs.
A green energy company employs erpoz strategies to drive innovation in sustainable practices. This approach not only maximizes operational efficiency but also fosters community engagement through eco-friendly initiatives. Each of these examples illustrates how diverse industries can harness erpoz for strategic advantage.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Implementing Erpoz
Implementing Erpoz offers several advantages for modern businesses. Its flexibility allows entrepreneurs to adapt strategies quickly in response to market changes. This agility can be a game-changer, especially in today’s fast-paced environment.
Another benefit is the emphasis on collaboration. Erpoz encourages teamwork across various departments, fostering innovation and creativity. When employees work together seamlessly, ideas flow more freely.
However, there are challenges too. The initial learning curve can be steep for teams unfamiliar with this approach. Transitioning to an Erpoz-driven strategy may require significant time and resources.
Additionally, not all companies thrive under this model. Some organizations might find it clashes with their existing structures or cultures, leading to potential resistance from staff who prefer traditional methods of operation.
Understanding both the benefits and drawbacks is crucial before fully integrating Erpoz into your business framework.
How Entrepreneurs Can Incorporate Erpoz into Their Business Plans?
Incorporating erpoz into business plans can be a transformative step for entrepreneurs. Start by identifying key areas where this concept aligns with your current strategy. Analyze your market and customer needs.
Next, integrate erpoz’s principles into your value proposition. This could mean rethinking how you deliver products or services to create more value for customers.
Encourage collaboration within teams to foster innovative ideas inspired by erpoz’s. It’s vital that every department understands its potential impact on overall goals.
Utilize technology to streamline processes influenced by erpoz’s concepts. Automation and data analysis tools can enhance efficiency while reducing costs.
Keep an open line of communication with stakeholders about changes stemming from the integration of erpoz’s. Their feedback will be invaluable in refining strategies over time.
Conclusion: The Future of Erpoz in the World of Entrepreneurship
The future of erpoz’s in the world of entrepreneurship looks bright and filled with potential. As businesses increasingly seek innovative approaches to maintain competitiveness, erpoz’s offers a fresh perspective. It encourages adaptability, fostering an environment that embraces change rather than fearing it.
Entrepreneurs who leverage erpoz’s can create more resilient business models. They can respond swiftly to market dynamics while ensuring their strategies remain aligned with consumer needs and technological advancements. The integration of erpoz’s into various sectors shows its versatility and relevance.
As we move forward, the principles underpinning erpoz’s will likely become essential tools for entrepreneurs seeking not just survival but growth in a rapidly evolving marketplace. Embracing this emerging idea could very well define successful entrepreneurial journeys in the years ahead.
TECHNOLOGY
dandork63: Mystery, Meaning, and Rise of a Digital Alias

Introduction to the Dandork63
In the vast expanse of the digital world, where usernames and avatars often blend into an endless sea of anonymity, one name stands out: dandork63. A curious combination that evokes both intrigue and playfulness, this alias has garnered a devoted following across various social media platforms. But what lies behind this enigmatic moniker? As we delve deeper into the mystery surrounding dandork63, we’ll explore its origins, influence, and the growing fascination with digital identities in our interconnected lives. Prepare to embark on a journey that uncovers not just a username but also the essence of modern online existence.
The mysterious origins of the name
The name “dandork63” sparks curiosity at first glance. Where did it come from? What does it mean?
Some speculate that “dandork” combines playful elements of the word “dandy” and a nod to nerdy culture, creating an intriguing persona that feels both charming and quirky. The number 63 adds another layer of mystery—perhaps a birth year, a favorite number, or even an inside joke.
Others believe the name is deliberately ambiguous. It invites questions while offering little in return, embodying the essence of many digital aliases today.
This combination makes dandork63 memorable and approachable yet enigmatic enough to keep followers guessing. Each time someone mentions it, they add another thread to its complex tapestry of meaning and identity. As fans delve into this moniker’s origins, they can’t help but feel drawn deeper into its enigma.
Dandork63’s presence on social media and online platforms
Dandork63 has established a distinctive presence across multiple social media platforms. With an engaging presence, this digital alias captivates audiences with witty commentary and visually striking content.
From Twitter to Instagram, Dandork63’s posts often blend humor with thought-provoking insights. Followers are drawn in by the authenticity that radiates from each update.
On TikTok, short videos showcase creativity and spontaneity, further boosting the persona’s reach. The algorithms favor engaging content, and Dandork63 knows how to play the game well.
YouTube offers another avenue where intricate storytelling meets vibrant visuals. This platform allows for deeper connections through longer narratives that resonate with viewers.
Engagement is key, and comments flood in as fans eagerly discuss recent uploads. This interaction fosters a sense of community around Dandork63’s brand a testament to the power of digital communication today.
The rise in popularity and following of dandork63
The surge in popularity of dandork63 has been nothing short of remarkable. Initially, this digital alias captured attention through quirky posts and relatable content that resonated with many.
As social media platforms exploded, so did the reach of dandork63. Engaging visuals combined with a distinct voice helped cultivate a loyal following. Fans began sharing their own experiences inspired by the account, creating an organic growth cycle.
Community interaction played a crucial role too. Followers felt connected to both the persona and each other. Memes, comments, and shares amplified visibility across various networks.
What sets dandork63 apart is an authenticity that’s hard to replicate. This unique blend has turned casual observers into passionate fans eager for more compelling content from this mysterious figure online.
Speculations on the true identity behind dandork63
The identity of dandork63 has sparked countless theories. Some believe it’s a tech-savvy individual with a knack for humor. Others speculate it’s a collective, an entire team behind the username.
Social media sleuths have combed through posts and interactions, searching for clues. They analyze the writing style, looking for hints that might reveal more about this enigmatic persona.
A few fans even suggest that dandork63 could be an established influencer in disguise, testing waters under a pseudonym to gauge reactions without the weight of their fame.
Then there are conspiracy theorists who think there’s something deeper at play—a secret society or underground group using this alias as a front to share hidden knowledge.
Each theory adds another layer to the mystery surrounding dandork63, captivating audiences and keeping them guessing about who—or what—lies beneath the surface of this digital enigma.
The impact and influence of digital aliases in today’s society
Digital aliases like dandork63 have revolutionized online interactions. They offer a canvas for self-expression, free from societal constraints tied to real identities. This anonymity fosters creativity and experimentation.
People can explore different facets of their personality without fear of judgment. It encourages authenticity in ways that traditional social norms might stifle. With each alias comes a unique voice, adding diversity to the digital landscape.
These personas also shape communities. Users often rally around shared interests or values attached to these names. Whether it’s humor, art, or gaming, digital aliases create connections that transcend geographical boundaries.
Furthermore, they play a significant role in activism and commentary. Individuals can tackle sensitive topics while protecting their personal lives. This has enabled discussions that might otherwise remain silenced in public forums.
As our world becomes increasingly interconnected through technology, the allure and impact of digital aliases continue to grow stronger.
Conclusion: The enigma of dandork63 continues to fascinate and inspire others to create their own digital
The enigma of dandork63 continues to captivate the digital landscape. This alias has sparked curiosity, inspiring many to explore their own online identities. The allure lies not just in the mystery but also in how people connect through shared interests and creativity.
As social media evolves, so does the significance of unique identifiers like dandork63. These aliases allow individuals to express themselves freely while maintaining a layer of anonymity. They serve as gateways for meaningful interactions and communities.
Dandork63 has become more than just a name; it represents a movement towards embracing individuality in an often homogenized digital world. As followers grow, so does the intrigue surrounding this persona proving that sometimes, it’s not about who you are but what you stand for that truly matters.
This ongoing fascination with digital aliases reflects our collective desire to innovate and redefine ourselves online. Dandork63 is merely one example among many compelling figures emerging from virtual spaces a testament to the endless possibilities waiting to be explored by anyone daring enough to create their own path.

 HOME IMPROVEMENT12 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT12 months agoThe Do’s and Don’ts of Renting Rubbish Bins for Your Next Renovation

 BUSINESS1 year ago
BUSINESS1 year agoExploring the Benefits of Commercial Printing

 BUSINESS1 year ago
BUSINESS1 year agoBrand Visibility with Imprint Now and Custom Poly Mailers

 TECHNOLOGY11 months ago
TECHNOLOGY11 months agoDizipal 608: The Tech Revolution Redefined

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoThe Surprising Benefits of Weight Loss Peptides You Need to Know

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoYour Guide to Shedding Pounds in the Digital Age

 HOME IMPROVEMENT8 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT8 months agoGet Your Grout to Gleam With These Easy-To-Follow Tips

 HEALTH11 months ago
HEALTH11 months agoHappy Hippo Kratom Reviews: Read Before You Buy!












