HEALTH
12 Common Triggers for Addiction and How to Avoid Them

Understanding and avoiding common triggers is essential for maintaining sobriety during addiction recovery. Triggers can lead to cravings and relapse if not managed effectively.
1. Stress
Stress is one of the most common triggers for addiction. High levels of stress can lead to cravings as individuals seek relief through substance use.
How to Avoid It:
Practice stress management techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity. Prioritize self-care and seek support from friends, family, or a therapist to help manage stress effectively.
2. Social Pressure
Social situations where others are using substances can be challenging for someone in recovery. Peer pressure can tempt you to join in and relapse.
How to Avoid It:
Surround yourself with supportive, sober friends. Politely decline invitations to events where substance use will be present. Plan alternative activities with friends who respect your commitment to sobriety.
3. Emotional Distress
Feelings of sadness, anger, or loneliness can trigger cravings for substances as a way to cope with negative emotions.
How to Avoid It:
Develop healthy coping mechanisms such as journaling, talking to a therapist, or engaging in a hobby. Build a strong support network to lean on during times of emotional distress.
4. Environmental Cues
Certain places, people, or situations associated with past substance use can trigger cravings.
How to Avoid It:
Identify and avoid high-risk environments that remind you of your substance use. Create new, positive associations by spending time in supportive, sober settings.
5. Celebrations and Holidays
Special occasions often involve substance use, which can be a trigger for those in recovery.
How to Avoid It:
Plan ahead for celebrations and holidays by bringing your own non-alcoholic beverages and having an exit strategy if you feel uncomfortable. Attend sober events or host your own celebrations without substances.
6. Fatigue
Being overly tired can lower your defenses and make it harder to resist cravings.
How to Avoid It:
Prioritize getting enough sleep and establish a regular sleep routine. Listen to your body and rest when needed to maintain physical and mental health.
7. Boredom
Idle time and lack of stimulation can lead to thoughts of substance use as a way to pass the time.
How to Avoid It:
Stay busy with activities that interest you, such as hobbies, exercise, or volunteering. Create a daily schedule to keep yourself engaged and productive.
8. Relationship Problems
Conflict and tension in relationships can trigger emotional distress and cravings.
How to Avoid It:
Practice open communication and seek therapy to address relationship issues. Surround yourself with supportive people who respect your recovery journey.
9. Physical Pain
Chronic pain or discomfort can lead to the temptation to use substances for relief.
How to Avoid It:
Work with healthcare professionals to manage pain through non-addictive medications and alternative therapies such as physical therapy, acupuncture, or mindfulness.
10. Financial Stress
Worrying about money can create significant stress, leading to cravings.
How to Avoid It:
Create a budget and seek financial advice to manage your finances effectively. Focus on building financial stability and seek support from friends, family, or financial counselors.
11. Celebrating Milestones
Ironically, achieving significant milestones in recovery can sometimes trigger thoughts of “rewarding” yourself with substances.
How to Avoid It:
Celebrate milestones in healthy, substance-free ways. Treat yourself to a special outing, a new hobby, or a meaningful experience that reinforces your commitment to sobriety.
12. Complacency
Becoming too comfortable in your recovery can lead to overconfidence and a lapse in vigilance, increasing the risk of relapse.
How to Avoid It:
Stay committed to your recovery routine and continue attending support groups and therapy sessions. Regularly review your goals and progress to stay focused on your sobriety.
Strategies for Managing Triggers
While avoiding triggers entirely may not always be possible, having strategies in place can help you manage them effectively. Here are some additional tips for managing triggers:
1. Develop a Relapse Prevention Plan
Create a detailed plan that outlines how you will handle triggers and cravings. Include specific strategies, coping mechanisms, and emergency contacts. Having a plan in place provides a sense of security and readiness.
2. Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness involves staying present and aware of your thoughts and feelings without judgment. Practicing mindfulness can help you recognize triggers early and respond to them in a healthy way.
3. Build a Support Network
Surround yourself with supportive friends, family, and peers who understand your journey and can provide encouragement and accountability. Regularly attend support group meetings to stay connected and motivated.
4. Engage in Healthy Activities
Regular exercise, hobbies, and other positive activities can provide a healthy distraction from cravings. Engaging in activities that you enjoy helps build a fulfilling, sober lifestyle.
5. Seek Professional Help
Therapists and counselors can provide valuable support and guidance in managing triggers. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can help you develop effective coping strategies.
6. Reflect and Adjust
Regularly reflect on your progress and the effectiveness of your strategies. Adjust your plan as needed based on your experiences and challenges. Continuous self-awareness and adaptability are key to maintaining sobriety.
7. Stay Educated
Educate yourself about addiction and recovery. Understanding the science behind addiction and learning about different recovery strategies can empower you to make informed decisions about your health.
8. Practice Self-Care
Prioritize self-care to maintain your physical and mental health. Taking care of yourself ensures you have the energy and resilience to handle triggers effectively.
9. Celebrate Progress
Acknowledge and celebrate your achievements, no matter how small. Recognizing your progress reinforces positive behavior and motivates you to continue your recovery journey.
HEALTH
Sourthrout: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Care Tips
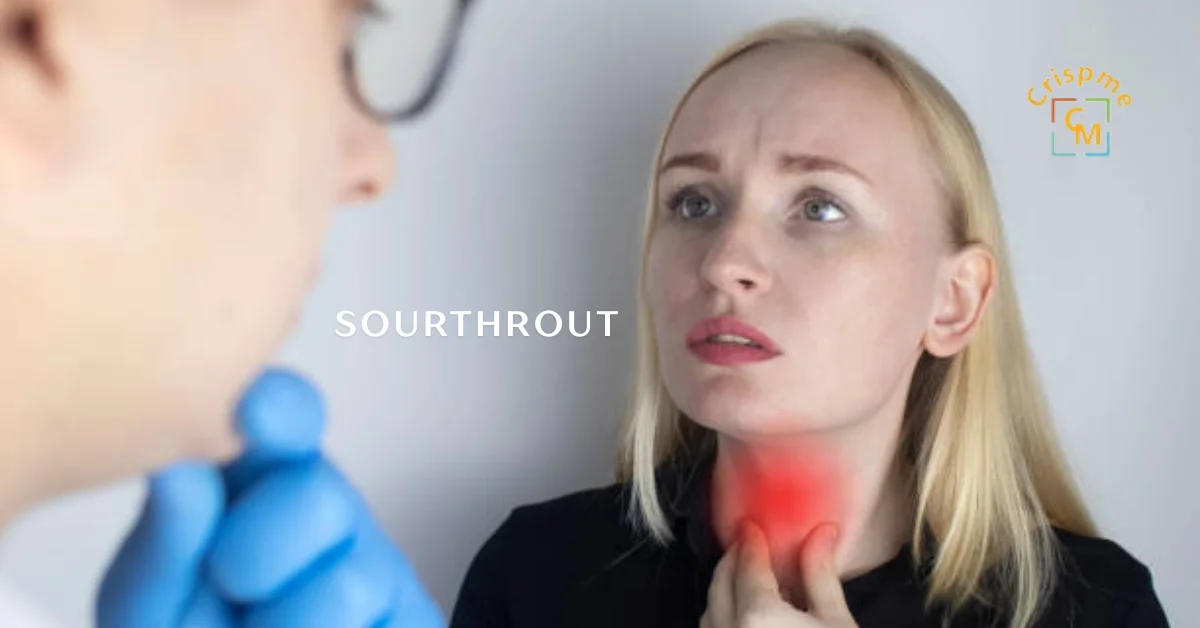
Sourthrout is a condition that many people might not be familiar with, but it can cause discomfort and distress for those who experience it. Imagine trying to go about your day while dealing with an annoying sore throat that just won’t quit. It can make swallowing difficult and even affect your voice. Understanding sourthrout is crucial to managing its symptoms effectively.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into what sourthrout really is, explore the causes behind it, and identify the common symptoms you should watch out for. We will also discuss how healthcare professionals diagnose this condition, provide treatment options available to alleviate discomfort, and share prevention measures you can take to reduce your risk of developing sourthrout in the first place. Plus, we’ll offer some home remedies and care tips that could help soothe your throat at home.
Being knowledgeable gives you greater control over managing your well-being. Let’s unravel the mystery of sourthrout together!
What is Sourthrout?
Sourthrout, often described as a persistent sore throat, can be more than just an irritation. It’s characterized by inflammation in the throat area, leading to discomfort and difficulty swallowing.
This condition can arise from various underlying issues, including viral infections like the common cold or more serious bacterial infections such as strep throat. Allergies and environmental factors may also play a role.
While it is not a medical term you’ll find in every textbook, sourthrout captures the experience of those who suffer through its symptoms regularly. People may describe it as scratchy or raw – sensations that make even simple tasks challenging.
Understanding what sourthrout entails helps individuals recognize when they need to seek further care or adopt self-management strategies for relief.
Causes and Symptoms of Sourthrout
Sourthrout, commonly recognized for its discomforting symptoms, can stem from various causes. Viral infections are often the primary culprits. Many people experience sourthrout after catching a cold or flu.
Bacterial infections also play a significant role. Streptococcus bacteria can lead to strep throat, causing intense soreness and inflammation.
Allergies and irritants might contribute too. Dust, pollen, or smoke can trigger an overreaction in your throat tissues.
Common symptoms include persistent pain while swallowing and scratchiness that may worsen throughout the day. You might notice redness or swelling in the back of your throat as well.
Sometimes sourthrout comes with other signs like fever or swollen lymph nodes. Each symptom creates a unique combination that helps identify this condition’s severity and underlying cause.
Diagnosis of Sourthrout
Diagnosing sourthrout typically begins with a thorough evaluation of symptoms. A healthcare provider will inquire about your medical history and conduct a physical examination.
They may inspect your throat for signs of inflammation or swelling. Looking for patches, redness, or other unusual characteristics can help pinpoint the problem.
At times, additional examinations are required to verify the exact condition. This might include throat cultures or rapid antigen tests to determine if bacteria are present.
Blood tests could also be recommended to rule out other underlying conditions that mimic sourthrout symptoms.
Staying proactive during this process is vital. Clear communication with your healthcare provider ensures accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment options later on.
Treatment Options for Sourthrout
When it comes to treating sourthrout, various options are available depending on the severity and underlying cause. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help ease discomfort and reduce inflammation.
When bacteria are believed to be the cause, a medical professional might recommend an antibiotic course. Always follow their guidance for dosage and duration to ensure effectiveness.
For viral infections, treatment usually focuses on symptom management. Gargling warm salt water can provide soothing relief while staying hydrated is crucial for recovery.
Medicated drops or throat mists can provide short-term soothing relief. They work by numbing the throat area, making swallowing less painful.
In some cases, steroids may be recommended to decrease swelling in severe situations. However, this option should always be discussed with a medical professional before use.
Prevention Measures for Sourthrout
Preventing sourthrout starts with maintaining good oral hygiene. Maintain oral cleanliness by brushing morning and evening and cleaning between teeth consistently. This helps to eliminate bacteria that contribute to throat issues.
Keep your body well supplied with fluids by sipping water regularly from morning to night. Keeping your throat moist can reduce irritation and discomfort caused by dry air or allergens.
Avoid irritants like smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke, as these can aggravate the throat lining. Additionally, limit alcohol consumption, which may also lead to throat dryness.
Practice good hand hygiene, especially during cold and flu season. Wash your hands frequently to prevent infections that could trigger sourthrout symptoms.
Consider using a humidifier in your home. Increasing humidity indoors may relieve throat dryness and support healthier breathing.
Home Remedies and Care Tips for Managing Sourthrout?
Managing sour throat discomfort can often be addressed with simple home remedies. Warm salt water gargles are a classic solution, helping to reduce inflammation and soothe irritation.
Honey is another natural option. It has antibacterial properties and can coat the throat, providing relief when ingested or mixed into herbal teas.
Staying hydrated is crucial; drinking plenty of fluids keeps the throat moist and aids in recovery. Warm infusions made with ginger or chamomile may help calm and ease throat discomfort.
Steam inhalation may also help relieve congestion and ease swallowing difficulties caused by a sore throat. A hot shower can work wonders too!
Resting your voice allows your vocal cords to heal faster, so try to minimize talking whenever possible.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Sourthrout
Recognizing when to seek medical attention for sourthrout is crucial. If you experience severe pain that disrupts your daily activities, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
Fever can also signal a more serious issue. A high temperature, particularly if persistent, should prompt a visit to your doctor.
If the discomfort lasts longer than a week or worsens over time, don’t hesitate to get help. Chronic symptoms may indicate an underlying condition requiring further evaluation.
Additionally, difficulty swallowing or breathing warrants immediate medical assistance. These are signs that could lead to complications if left untreated.
In any case where home remedies aren’t providing relief or symptoms escalate quickly, seeking guidance from a healthcare provider is essential for proper care and peace of mind.
Conclusion
Sourthrout can be an uncomfortable condition that affects many people at different stages of life. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial in managing this ailment effectively. By staying informed about prevention measures and incorporating home remedies into your routine, you can minimize the impact of sourthrout on your daily activities.
If you experience persistent symptoms or if they worsen over time, seeking professional medical advice is essential. Being proactive about your health ensures that any underlying issues are addressed promptly. With the right approach to care and management, living with sourthrout doesn’t have to disrupt your quality of life. Stay educated and attentive to how your body responds to various treatments for optimal wellbeing.
HEALTH
Hyperfiksaatio: The Psychology of Locked-In Focus
Introduction to Hyperfiksaatio
Have you ever found yourself so absorbed in a task that the world around you fades away? This phenomenon, known as hyperfiksaatio, can feel both exhilarating and overwhelming. It’s that intense focus where distractions disappear, but sometimes it leads to neglecting other important aspects of life. Understanding hyperfiksaatio is essential not only for maximizing productivity but also for maintaining balance in our daily routines. Let’s explore this intriguing psychological concept and uncover its effects on our minds and lives.
What is Locked-In Focus?
Locked-In Focus is a mental state where an individual becomes intensely absorbed in a particular task or idea. This hyperfiksaatio can create a tunnel vision effect, making it difficult to shift attention elsewhere.
When someone experiences locked-in focus, distractions often fade away. Time may seem irrelevant as one dives deeper into the subject at hand. This state can feel exhilarating but also limiting.
While some people thrive under this concentrated energy, others might struggle with its effects. The inability to divert attention can lead to neglecting other responsibilities or personal needs.
Understanding locked-in focus helps clarify how our minds work during periods of deep concentration. It’s important to recognize when this intense focus serves us well and when it might become counterproductive.
The Symptoms and Signs of Hyperfiksaatio
Hyperfiksaatio manifests through a variety of symptoms that can be quite distinct. Individuals may find themselves consumed by a single thought or task, unable to shift their attention elsewhere. This intense focus often leads to neglecting other responsibilities.
People experiencing hyperfiksaatio might lose track of time. What starts as a productive session can quickly extend into hours without breaks. Sleep and meals may become afterthoughts, further illustrating the depth of this fixation.
Emotional signs also accompany this state. Frustration arises when distractions occur, leading to heightened stress levels. The mind becomes fixated on achieving perfection in the chosen subject, causing anxiety if progress seems insufficient.
Social interactions often take a hit too; friends and family might notice withdrawal from conversations or activities due to overwhelming concentration on an obsession. Recognizing these indicators is key for anyone navigating this psychological landscape.
Causes and Effects of Hyperfiksaatio
Hyperfiksaatio often emerges from a blend of personal, environmental, and psychological factors. High levels of stress or anxiety can trigger an intense focus on specific thoughts or tasks. This fixation may serve as a coping mechanism to escape overwhelming emotions.
Certain personality traits also play a role. Individuals who are detail-oriented or perfectionistic may find themselves drawn into hyperfiksaatio more easily than others.
On the flip side, the effects can be both positive and negative. While it might lead to heightened productivity in short bursts, extended periods of locked-in focus can result in burnout and fatigue. Relationships may suffer too, as social interactions take a back seat during these episodes.
Additionally, mental health conditions such as ADHD or OCD often intertwine with hyperfiksaatio, complicating daily functioning further. Understanding these dynamics is essential for managing their impact effectively.
Coping Mechanisms for Dealing with Locked-In Focus
Coping with hyperfiksaatio can be a challenge, but practical strategies exist to help regain balance. Start by setting time limits for focused activities. Use timers to create structured breaks. These intervals allow your mind to reset and shift gears.
Engaging in physical activity is another effective approach. A brisk walk or quick workout clears the mental fog and re-energizes you. Movement stimulates endorphins, enhancing mood and clarity.
Mindfulness techniques also prove beneficial. Meditation or deep-breathing exercises ground your thoughts and promote relaxation. Even a few minutes of focused breathing can ease tension.
Consider journaling as well; it encourages self-reflection. Writing down thoughts helps externalize them, reducing their grip on your focus.
Maintain social connections. Engaging with others offers fresh perspectives and reminds you that there’s more beyond the current obsession.
The Connection Between Hyperfiksaatio and Productivity
Hyperfiksaatio can be a double-edged sword when it comes to productivity. On one hand, intense focus allows individuals to dive deep into tasks, leading to remarkable results. This concentrated effort often produces high-quality work in less time.
However, this locked-in focus may also come at a cost. It can create blind spots that prevent you from seeing the bigger picture or addressing other important responsibilities. The all-consuming nature of hyperfiksaatio might lead to neglecting social interactions or self-care.
Moreover, while driving efficiency in specific projects, it can hinder flexibility and adaptability. When your mind is solely fixated on one task, shifting gears becomes challenging.
Understanding this connection is crucial for harnessing the positive aspects of hyperfiksaatio while mitigating its potential downsides. Finding the right balance between focused work and broader awareness plays a significant role in achieving sustainable productivity levels.
Strategies for Breaking Out of Locked-In Focus
Breaking out of hyperfiksaatio requires intentional effort and self-awareness. Start by setting time limits on your tasks. This creates a sense of urgency, nudging you to shift focus when the timer goes off.
Incorporate regular breaks into your routine. A quick walk or stretching session can clear your mind and refresh your perspective. These small intervals help reset your mental state.
Mindfulness techniques also play a crucial role. Practices like deep breathing or meditation can ground you, making it easier to step back from obsessive thoughts.
Consider changing your environment as well. A new workspace or even rearranging furniture can stimulate creativity and break the cycle of locked-in focus.
Engaging with others is essential too. Sharing ideas or discussing challenges with colleagues can pull you away from narrow thinking patterns, fostering collaboration and innovation instead of fixation.
Conclusion: Embracing a Balanced Approach
Finding a balance is essential when it comes to hyperfiksaatio. While locked-in focus can enhance productivity and drive creativity, it also has its downsides. It’s important to recognize the fine line between deep concentration and becoming overly consumed by a single thought or task.
Embracing variety in our activities can prevent us from becoming trapped in cycles of fixation. Incorporating breaks, exploring new interests, or even practicing mindfulness can help create a more balanced mental state. This way, we maintain the benefits of hyperfiksaatio while avoiding its pitfalls.
Understanding how to navigate this complex psychological phenomenon allows us to harness our focus without losing sight of the bigger picture. Adopting strategies that promote flexibility ensures we remain productive yet adaptable in an ever-changing world.
HEALTH
Helpful Tips for Those Suffering With Chronic Pain

Living with chronic pain can be a crippling and stressful experience that affects all facets of your life, including your mental and physical health. Regaining control over your pain is crucial, regardless of whether you have fibromyalgia, arthritis, chronic back pain, or any ailment that causes you discomfort.
Understanding Your Pain and Its Causes
Understanding your pain and its underlying causes is the first step toward properly treating chronic pain. Numerous things, such as trauma, inflammation, nerve damage, or underlying medical disorders, can cause chronic pain. Consider the location, degree, duration, and any triggers or mitigating variables for your pain as you take some time to evaluate your symptoms. To monitor your symptoms and spot any trends or triggers that could be aggravating your pain, keep a pain diary. Understanding the underlying causes of your pain will enable you to collaborate with medical specialists to create a customized treatment plan that takes into account your unique requirements and concerns.
Exploring Treatment Options and Therapies
Investigate different therapy and treatment options that can help reduce your symptoms and enhance your quality of life as soon as you have a better knowledge of your pain and its underlying causes. Treatment options can include prescription or over-the-counter drugs, physical therapy, chiropractic care, acupuncture, massage therapy, or nerve blocks, depending on the kind and intensity of your pain. Furthermore, by encouraging relaxation, lowering stress, and enhancing general well-being, complementary and alternative treatments, including yoga, tai chi, meditation, and mindfulness-based stress reduction approaches, can provide further relief from chronic pain.
Incorporating Lifestyle Modifications for Pain Management
Lifestyle changes can be quite helpful in controlling chronic pain and enhancing your general well-being, in addition to medical therapies and treatments. Make self-care routines that support both physical and mental well-being a priority, such as consistent exercise, a balanced diet, enough sleep, and stress reduction. Walking, swimming, or cycling are examples of low-impact workouts that can enhance cardiovascular health, flexibility, and strength without increasing the chance of injury or worsening discomfort. To promote optimum nutrition and lower inflammation, keep a well-balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats. Use stress-reduction methods to ease your mind and release tension, which can aggravate pain sensations. Some of these methods include progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing, and guided imagery.
Building a Support Network and Seeking Professional Help
It might be lonely to live with chronic pain, but you don’t have to go through this path by yourself. Creating a network of friends, family, and medical professionals who can relate to your experiences can be very helpful in terms of both practical support and emotional support. Seek support, empathy, and company from your loved ones, and don’t be afraid to ask for assistance when required with everyday duties or obligations. Consider joining online forums or support groups for people with chronic pain as well. These spaces allow you to interact with others who have experienced similar things, share resources and information, and provide encouragement and support to one another.
Going to a Clinic for Specialized Care
Consider obtaining specialist care at a pain management clinic if you’ve tried a variety of therapies and interventions but are still unable to find relief from chronic pain. Pain management clinics are specialized medical establishments manned by medical specialists with expertise in the diagnosis and treatment of persistent pain disorders, so it’s important to find a Chicago headache clinic or one in your area depending on what type of pain you are experiencing. These clinics provide thorough assessments, individualized treatment programs made to meet the specific requirements of each patient, and diagnostic testing. Medication management, interventional techniques, physical therapy, psychiatric counseling, and complementary and alternative treatments are a few possible treatment choices. Furthermore, access to multidisciplinary care teams—which include pain experts, physical therapists, psychiatrists, and nutritionists—who work together to address the intricate and multidimensional nature of chronic pain is often made possible by pain management clinics.
Conclusion
Although managing chronic pain can be difficult, it’s important to keep in mind that there are helpful treatment choices and tactics available to assist you in finding relief and enhancing your quality of life. You’re not alone. In your quest for pain treatment, keep in mind to be persistent and patient, and don’t be afraid to ask for assistance when you need it. You can experience relief from chronic pain and lead a more active, fulfilling life without having to worry about being in pain all the time with commitment and assistance.

 BUSINESS1 year ago
BUSINESS1 year agoExploring the Benefits of Commercial Printing

 HOME IMPROVEMENT12 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT12 months agoThe Do’s and Don’ts of Renting Rubbish Bins for Your Next Renovation

 BUSINESS12 months ago
BUSINESS12 months agoBrand Visibility with Imprint Now and Custom Poly Mailers

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoThe Surprising Benefits of Weight Loss Peptides You Need to Know

 TECHNOLOGY10 months ago
TECHNOLOGY10 months agoDizipal 608: The Tech Revolution Redefined

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoYour Guide to Shedding Pounds in the Digital Age

 HOME IMPROVEMENT8 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT8 months agoGet Your Grout to Gleam With These Easy-To-Follow Tips

 HEALTH11 months ago
HEALTH11 months agoHappy Hippo Kratom Reviews: Read Before You Buy!












