HEALTH
7 Features of ADHD Testing

ADHD testing involves a series of evaluations with doctors, teachers, and professionals to diagnose this disorder. It’s a multi-step process assessing symptoms like attention and hyperactivity. Diagnosis in adults is determined by the number and severity of symptoms and their duration. Here are some of the features of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder testing:
1. Comprehensive Clinical Evaluations
A mental health professional will gather detailed information about your background, symptoms, and experiences. This involves interviewing you and potentially a parent, partner, or teacher to get a well-rounded perspective. The clinician will also review medical records and any relevant history that contributes to symptoms. This comprehensive evaluation helps determine if ADHD is the correct diagnosis. The patient undergoes a physical examination to rule out any other possible causes for symptoms.
2. Behavioral and Developmental Assessments
Your doctor or therapist will use various behavioral and developmental assessments to evaluate ADHD symptoms. This includes questionnaires that measure attention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and executive functioning skills. These assessments help identify specific behaviors and areas of difficulty that may indicate ADHD. The results of these assessments help professionals develop a personalized treatment plan. When conducting these assessments, provide honest and accurate responses to get a precise diagnosis.
3. Symptom Rating Scales
Symptom rating scales are used to measure the severity of ADHD symptoms and their impact on daily functioning. These scales can be completed by the patient, parent, or teacher and provide a quantitative measure of ADHD symptoms. The scores obtained from these rating scales may help determine the severity of ADHD and monitor progress during treatment. ADHD testing often includes multiple symptom rating scales to gather a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s symptoms. Checklists may be used in conjunction with or instead of symptom rating scales. These are lists of specific behaviors and symptoms associated with ADHD that may be checked off if present.
4. Executive Functioning Assessments
Executive functioning refers to a set of cognitive skills that help individuals plan, manage time, organize information, and regulate their behavior. Individuals with ADHD often struggle with executive functioning skills, which may impact their academic or work performance. Specific executive functioning assessments can be used to assess these skills. These assessments typically involve organization and planning exercises, time management activities, and problem-solving tasks. The results of these assessments provide valuable information about an individual’s executive functioning abilities and may guide interventions to improve these skills.
5. Medical History Review
Reviewing your medical history helps rule out other potential explanations for your symptoms. This might involve examining past diagnoses and any medications you’re currently taking. Share any relevant information about your medical history with your healthcare provider. This can include any previous treatment for ADHD or other mental health conditions and any family history of ADHD or other disorders. The more information your healthcare provider has, the better they can understand your symptoms and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Reviewing your medical history also allows professionals to diagnose other underlying medical conditions.
6. Screening for Co-occurring Conditions
The symptoms of ADHD can often co-occur with other conditions, such as anxiety or learning disabilities. Screening for these conditions involves questionnaires or assessments specific to the condition in question. Identifying and treating these co-occurring conditions can improve overall functioning and quality of life for individuals with ADHD. The presence of co-occurring conditions may also impact the type and effectiveness of treatment recommended for ADHD.
7. Psychological Testing
If ADHD is suspected, your healthcare provider may refer you for psychological testing. This assessment involves a series of standardized tests and measures to evaluate various aspects of cognitive functioning, including attention, memory, and problem-solving skills. These results can help determine if any underlying cognitive deficits are contributing to ADHD symptoms. Psychological testing identifies the different types of executive functioning skills that may be affected by ADHD, such as planning, organization, and self-control. This information can help develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
Get Started With Treatment Through ADHD Testing
ADH testing helps to diagnose ADHD and identify any underlying factors that may be contributing to symptoms. After working with a healthcare provider, individuals with ADHD can develop individualized treatment plans that include medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Regular monitoring and reassessment will help them track progress and adjust the treatment plan. Visit a reliable healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation if you suspect that you or a loved one has ADHD.
HEALTH
fiebrigen: Meaning, Medical Roots, and Fever-Linked Insights

Introduction to the term of Fiebrigen
Fiebrigen an intriguing term that may not be on everyone’s radar, yet it holds a wealth of knowledge within its syllables. As we navigate the complex world of health and medicine, understanding this word opens doors to deeper insights about fevers and their significance in our lives. Whether you’ve experienced a fever yourself or cared for someone who has, the connection between fiebrigen and fever research is worth exploring. Let’s delve into what makes fiebrigen an important concept in medical discussions today.
The origin and medical roots of the word
The term “fiebrigen” has intriguing roots that intertwine language and medicine. It stems from the Latin word “febris,” which translates to fever. This origin connects it deeply to the physiological responses of our bodies during illness.
In historical texts, fevers were often viewed as signs of underlying conditions or infections. Ancient physicians relied on observing febrile states to diagnose ailments, laying groundwork for modern medical practices.
Fiebrigen encapsulates this clinical perspective, highlighting not just a symptom but an essential biological mechanism. Understanding its lineage offers valuable insights into how fevers have been perceived throughout time—both feared and respected in equal measure.
Moreover, exploring this term reveals shifts in medical paradigms over centuries. As science advanced, so did our grasp of what causes these elevated temperatures and their implications for health management today.
Understanding fever and its causes
Fever is more than just a rise in body temperature. It acts as a natural defense mechanism, signaling that the immune system is hard at work. When faced with infections or other ailments, the brain triggers this response to create an environment less hospitable for pathogens.
Several factors can contribute to fever. Common culprits include bacterial and viral infections, but it can also arise from inflammatory conditions or heat exposure.
Not all fevers are created equal; their patterns and intensities vary greatly depending on the underlying cause. For instance, a mild fever may indicate something minor like a cold, while higher temperatures could signal serious health concerns.
Understanding these nuances helps in assessing when medical intervention might be necessary. Recognizing the type of fever you’re facing can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health management strategies.
Common misconceptions about fevers
Many people believe that a fever is inherently dangerous. In reality, it often serves as the body’s natural defense mechanism against infections. A raised body temperature can help fight off pathogens.
Another widespread misconception is that you should always treat a fever with medication. While reducing discomfort can be important, fevers are usually not harmful and may even be beneficial in certain cases.
Some think that all fevers require immediate medical attention. However, many mild to moderate fevers can resolve on their own without intervention.
People also assume that a higher fever means a more serious illness. This isn’t necessarily true; some minor ailments can cause significant increases in temperature while severe conditions might result in lower readings.
Understanding these misconceptions helps demystify the role of fever and encourages better responses to health issues when they arise.
How fiebrigen is linked to fever research?
Fiebrigen plays a pivotal role in modern fever research. It serves as a lens through which scientists explore the complexities of fever responses.
Researchers focus on fiebrigen to understand how the body regulates temperature during an illness. This term encapsulates various biochemical processes that trigger heat production, signaling immune activity.
Recent studies have revealed that fiebrigen is not just a response mechanism but also influences disease outcomes. By analyzing its effects, healthcare professionals can predict patient recovery trajectories more accurately.
Moreover, advancements in technology allow for deeper insights into how fiebrigen interacts with different pathogens. This knowledge could lead to innovative treatments and better management strategies for fevers related to infections.
Understanding the nuances of fiebrigen opens doors to new avenues in fever research and treatment protocols tailored for individual patients.
Latest findings and insights on fevers and their impact on health
Recent studies have revealed intriguing connections between fever and the body’s immune response. Research indicates that controlled fevers can enhance the efficacy of certain treatments, signaling a shift in how healthcare professionals view elevated temperatures.
Moreover, scientists are uncovering links between chronic low-grade fevers and various conditions such as autoimmune diseases. This highlights an important area for further investigation in understanding how persistent inflammation affects overall health.
Additionally, advancements in technology allow for more precise monitoring of fever patterns. Wearable devices now track temperature fluctuations, providing valuable data to both patients and doctors.
This evolving landscape of fever research underscores the need for a nuanced perspective on fiebrigen. As we gather more insights, it becomes increasingly clear that our approach to treating fevers may need re-evaluation based on emerging findings.
Conclusion: Embracing a comprehensive understanding of fiebrigen for improved healthcare outcomes
A deeper understanding of fiebrigen can significantly enhance our approach to health and wellness. By unraveling its meaning and medical roots, we open doors to better diagnostics and treatment strategies. Recognizing the complexities surrounding fever—its causes, misconceptions, and implications allows us to appreciate the nuances in patient care.
Recent research sheds light on how fevers play a critical role in signaling underlying conditions. As studies continue to evolve, they unveil new insights that could transform healthcare practices related to febrile responses.
Embracing this comprehensive understanding equips both healthcare providers and patients with valuable knowledge. It encourages proactive discussions regarding symptoms and treatments while fostering an environment for informed decision-making about health care options related to fiebrigen. The journey toward improved outcomes begins with awareness a step worth taking for anyone looking to navigate the intricate landscape of fever-related health matters effectively.
HEALTH
Onulife: A Complete Path to Balanced Health and Wellness

Getting Started with Onulife
Are you seeking a path to a healthier, more balanced life? Look no further than Onulife. This innovative approach to health and wellness is designed to transform not just your body but also your mind and spirit. In today’s fast-paced world, finding harmony can seem like an impossible task. But with Onulife, it becomes attainable. Imagine fueling your body with nutritious foods while moving it in ways that energize rather than exhaust you. Picture cultivating a positive mindset that fosters inner peace amidst life’s chaos.
Onulife empowers you to take charge of your well-being through its holistic framework, focusing on five essential pillars that create lasting change. Whether you’re looking to revamp your nutrition or deepen your connections within a supportive community, this journey is about more than just physical fitness it’s about thriving in every aspect of life.
Join us as we explore the principles behind Onulife and discover how each pillar can lead you toward balanced health and wellness. It’s time to embrace the possibility of living fully engaged in body, mind, and soul!
What is Balanced Health and Wellness?
Balanced health and wellness is a holistic approach to living. It transcends just physical fitness, incorporating mental and emotional well-being too.
True balance means recognizing the interconnectedness of body, mind, and spirit. Each aspect influences the others in profound ways. When one area struggles, it can impact overall quality of life.
Health isn’t merely the absence of illness; it’s about thriving. This includes enjoying nutritious foods, engaging in regular exercise, nurturing relationships, and embracing mindfulness practices.
Wellness involves making conscious choices each day that promote vitality. It’s about creating harmony within oneself while also fostering connections with others.
Achieving balanced health requires ongoing commitment and awareness. It’s not a destination but rather an evolving journey toward better living. Embracing this mindset allows individuals to cultivate resilience against life’s challenges while enhancing their everyday experiences.
The 5 Pillars of Onulife for a Balanced Life
Onulife revolves around five essential pillars that guide you toward a balanced life. Each pillar represents a vital aspect of health and wellness, working together harmoniously.
The first pillar is nutrition. It emphasizes the importance of fueling your body with wholesome foods. A well-balanced diet helps you feel energized and vibrant throughout the day.
The following step focuses on physical activity. Regular physical activity isn’t just about looking good; it enhances your mood, strengthens your heart, and boosts overall vitality.
Mindfulness follows as the third pillar. Cultivating a positive mindset can lead to inner peace and resilience against stressors in everyday life.
Sleep is often overlooked yet crucial for optimal functioning. Quality rest rejuvenates both body and mind, making it an indispensable part of wellness.
Community plays a significant role in Onulife’s philosophy. Building connections fosters support systems that encourage healthy habits while reducing feelings of isolation.
Nutrition: Providing Your Body with Healthy and Nourishing Foods
Nutrition is the foundation of a healthy life. It goes beyond just eating to satisfy hunger; it’s about choosing foods that enhance your well-being.
When you think about nutrition, consider what fuels your body best. Fresh fruits and vegetables are rich in essential vitamins and minerals. Whole grains provide sustained energy, while lean proteins help with muscle repair and growth.
Hydration plays a crucial role too. Drinking enough water can improve concentration and support bodily functions. Avoid processed foods high in sugars and unhealthy fats—they can leave you feeling sluggish.
Think of meals as opportunities to nourish yourself creatively. Experiment with colorful ingredients on your plate, making every bite enjoyable while boosting health at the same time.
Pay attention to your body’s cues that indicate when you are hungry or satisfied. With mindful eating habits, you’ll develop a more positive relationship with food that supports balanced living effortlessly.
Exercise: Engaging Your Body to Achieve Better Health
Physical activity forms a fundamental part of the Onulife approach to wellness. It’s not just about hitting the gym or running miles; it’s about finding joy in movement.
Engaging in regular physical activity boosts your mood and energy levels. Basic activities such as walking, dancing, or gardening can greatly support your overall well-being. These activities can elevate heart rates while also bringing a sense of fulfillment.
Consistency is key when integrating exercise into your life. Aim for at least 30 minutes a day, mixing cardio with strength training and flexibility exercises. This creates a balanced routine that supports diverse aspects of fitness.
Paying attention to your body’s signals is equally important. Embrace what feels good instead of pushing through pain or discomfort. When you prioritize enjoyment alongside effort, exercise transforms from a chore into an uplifting experience.
Remember, every step counts toward achieving optimal health within the framework of Onulife’s holistic approach to wellness.
Mindfulness: Cultivating a Positive Mindset for Inner Peace
Mindfulness is the skill of fully focusing on the current moment. It involves tuning into your thoughts, feelings, and surroundings without judgment. This habit encourages the development of a more optimistic and constructive way of thinking.
When you embrace mindfulness, stress diminishes. Daily worries fade as you learn to focus on the here and now. Simple techniques like deep breathing can ground you in moments of chaos.
Meditation is another powerful tool for fostering inner peace. Even just five minutes a day can create profound shifts in your mental landscape.
As you become more aware of your emotions, negative patterns may surface. Acknowledging them without criticism leads to growth and healing.
Incorporating mindfulness into daily routines transforms otherwise mundane tasks into opportunities for reflection and gratitude. Making time for this kind of awareness enriches life’s experiences significantly while promoting overall well-being within Onulife’s framework.
Sleep: The Importance of Quality Rest for Overall Wellbeing
Quality sleep is essential for maintaining overall health and wellness. It’s during these restful hours that our bodies repair, rejuvenate, and restore energy. Without sufficient sleep, both physical and mental functions can suffer.
Lack of rest can lead to increased stress levels, mood swings, and impaired cognitive abilities. This creates a ripple effect on daily activities and decision-making processes. Many people overlook how crucial sleep is in their journey toward balanced health.
Creating a calming bedtime routine helps signal to the body that it’s time to wind down. Simple practices like reading or meditating can enhance your chances of falling into deep slumber.
Investing in quality sleep means investing in yourself. Prioritizing this vital aspect of life allows you to wake up refreshed and ready to tackle whatever comes your way each day. Healthy rest paves the path for greater productivity and emotional resilience.
Community: Building Connections and Support for a Healthy Lifestyle
Building a strong community is essential for anyone striving for balanced health and wellness through Onulife. The connections we form with others provide support, encouragement, and motivation on our journey. Surrounding ourselves with like-minded individuals can help us stay accountable to our goals.
Whether it’s joining local fitness classes, participating in online forums, or simply spending time with friends who share similar health aspirations, these interactions create a positive environment. Engaging with others fosters a sense of belonging that enhances mental wellbeing as well.
Moreover, sharing experiences and challenges within a supportive group allows for the exchange of valuable insights. Celebrating each other’s successes reinforces the idea that we are all in this together. This unity not only strengthens individual resolve but also cultivates an uplifting atmosphere where everyone thrives.
By embracing community as part of your Onulife journey, you’ll find yourself more motivated and inspired to maintain healthy habits. These relationships become an integral part of achieving overall wellness reminding you that you’re never alone on this path toward better health.
HEALTH
Sourthrout: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Care Tips
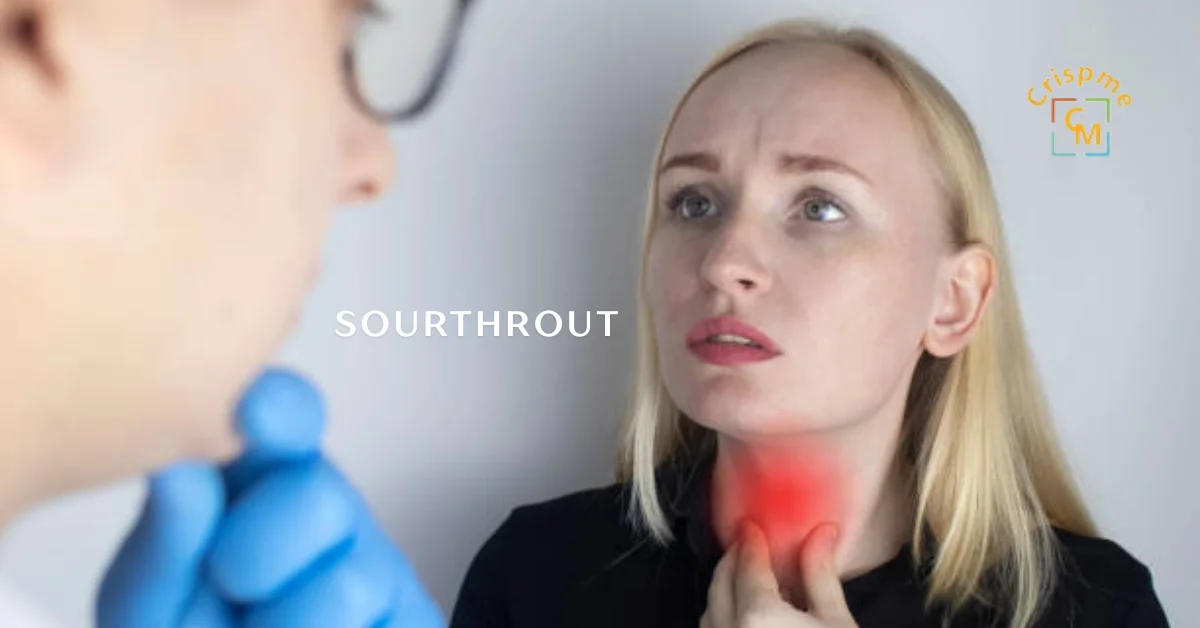
Sourthrout is a condition that many people might not be familiar with, but it can cause discomfort and distress for those who experience it. Imagine trying to go about your day while dealing with an annoying sore throat that just won’t quit. It can make swallowing difficult and even affect your voice. Understanding sourthrout is crucial to managing its symptoms effectively.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into what sourthrout really is, explore the causes behind it, and identify the common symptoms you should watch out for. We will also discuss how healthcare professionals diagnose this condition, provide treatment options available to alleviate discomfort, and share prevention measures you can take to reduce your risk of developing sourthrout in the first place. Plus, we’ll offer some home remedies and care tips that could help soothe your throat at home.
Being knowledgeable gives you greater control over managing your well-being. Let’s unravel the mystery of sourthrout together!
What is Sourthrout?
Sourthrout, often described as a persistent sore throat, can be more than just an irritation. It’s characterized by inflammation in the throat area, leading to discomfort and difficulty swallowing.
This condition can arise from various underlying issues, including viral infections like the common cold or more serious bacterial infections such as strep throat. Allergies and environmental factors may also play a role.
While it is not a medical term you’ll find in every textbook, sourthrout captures the experience of those who suffer through its symptoms regularly. People may describe it as scratchy or raw – sensations that make even simple tasks challenging.
Understanding what sourthrout entails helps individuals recognize when they need to seek further care or adopt self-management strategies for relief.
Causes and Symptoms of Sourthrout
Sourthrout, commonly recognized for its discomforting symptoms, can stem from various causes. Viral infections are often the primary culprits. Many people experience sourthrout after catching a cold or flu.
Bacterial infections also play a significant role. Streptococcus bacteria can lead to strep throat, causing intense soreness and inflammation.
Allergies and irritants might contribute too. Dust, pollen, or smoke can trigger an overreaction in your throat tissues.
Common symptoms include persistent pain while swallowing and scratchiness that may worsen throughout the day. You might notice redness or swelling in the back of your throat as well.
Sometimes sourthrout comes with other signs like fever or swollen lymph nodes. Each symptom creates a unique combination that helps identify this condition’s severity and underlying cause.
Diagnosis of Sourthrout
Diagnosing sourthrout typically begins with a thorough evaluation of symptoms. A healthcare provider will inquire about your medical history and conduct a physical examination.
They may inspect your throat for signs of inflammation or swelling. Looking for patches, redness, or other unusual characteristics can help pinpoint the problem.
At times, additional examinations are required to verify the exact condition. This might include throat cultures or rapid antigen tests to determine if bacteria are present.
Blood tests could also be recommended to rule out other underlying conditions that mimic sourthrout symptoms.
Staying proactive during this process is vital. Clear communication with your healthcare provider ensures accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment options later on.
Treatment Options for Sourthrout
When it comes to treating sourthrout, various options are available depending on the severity and underlying cause. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help ease discomfort and reduce inflammation.
When bacteria are believed to be the cause, a medical professional might recommend an antibiotic course. Always follow their guidance for dosage and duration to ensure effectiveness.
For viral infections, treatment usually focuses on symptom management. Gargling warm salt water can provide soothing relief while staying hydrated is crucial for recovery.
Medicated drops or throat mists can provide short-term soothing relief. They work by numbing the throat area, making swallowing less painful.
In some cases, steroids may be recommended to decrease swelling in severe situations. However, this option should always be discussed with a medical professional before use.
Prevention Measures for Sourthrout
Preventing sourthrout starts with maintaining good oral hygiene. Maintain oral cleanliness by brushing morning and evening and cleaning between teeth consistently. This helps to eliminate bacteria that contribute to throat issues.
Keep your body well supplied with fluids by sipping water regularly from morning to night. Keeping your throat moist can reduce irritation and discomfort caused by dry air or allergens.
Avoid irritants like smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke, as these can aggravate the throat lining. Additionally, limit alcohol consumption, which may also lead to throat dryness.
Practice good hand hygiene, especially during cold and flu season. Wash your hands frequently to prevent infections that could trigger sourthrout symptoms.
Consider using a humidifier in your home. Increasing humidity indoors may relieve throat dryness and support healthier breathing.
Home Remedies and Care Tips for Managing Sourthrout?
Managing sour throat discomfort can often be addressed with simple home remedies. Warm salt water gargles are a classic solution, helping to reduce inflammation and soothe irritation.
Honey is another natural option. It has antibacterial properties and can coat the throat, providing relief when ingested or mixed into herbal teas.
Staying hydrated is crucial; drinking plenty of fluids keeps the throat moist and aids in recovery. Warm infusions made with ginger or chamomile may help calm and ease throat discomfort.
Steam inhalation may also help relieve congestion and ease swallowing difficulties caused by a sore throat. A hot shower can work wonders too!
Resting your voice allows your vocal cords to heal faster, so try to minimize talking whenever possible.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Sourthrout
Recognizing when to seek medical attention for sourthrout is crucial. If you experience severe pain that disrupts your daily activities, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
Fever can also signal a more serious issue. A high temperature, particularly if persistent, should prompt a visit to your doctor.
If the discomfort lasts longer than a week or worsens over time, don’t hesitate to get help. Chronic symptoms may indicate an underlying condition requiring further evaluation.
Additionally, difficulty swallowing or breathing warrants immediate medical assistance. These are signs that could lead to complications if left untreated.
In any case where home remedies aren’t providing relief or symptoms escalate quickly, seeking guidance from a healthcare provider is essential for proper care and peace of mind.
Conclusion
Sourthrout can be an uncomfortable condition that affects many people at different stages of life. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial in managing this ailment effectively. By staying informed about prevention measures and incorporating home remedies into your routine, you can minimize the impact of sourthrout on your daily activities.
If you experience persistent symptoms or if they worsen over time, seeking professional medical advice is essential. Being proactive about your health ensures that any underlying issues are addressed promptly. With the right approach to care and management, living with sourthrout doesn’t have to disrupt your quality of life. Stay educated and attentive to how your body responds to various treatments for optimal wellbeing.

 HOME IMPROVEMENT12 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT12 months agoThe Do’s and Don’ts of Renting Rubbish Bins for Your Next Renovation

 BUSINESS1 year ago
BUSINESS1 year agoExploring the Benefits of Commercial Printing

 BUSINESS1 year ago
BUSINESS1 year agoBrand Visibility with Imprint Now and Custom Poly Mailers

 TECHNOLOGY11 months ago
TECHNOLOGY11 months agoDizipal 608: The Tech Revolution Redefined

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoThe Surprising Benefits of Weight Loss Peptides You Need to Know

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoYour Guide to Shedding Pounds in the Digital Age

 HOME IMPROVEMENT8 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT8 months agoGet Your Grout to Gleam With These Easy-To-Follow Tips

 HEALTH11 months ago
HEALTH11 months agoHappy Hippo Kratom Reviews: Read Before You Buy!












