HEALTH
The Long-Term Impact of Untreated Childhood Astigmatism in Adulthood
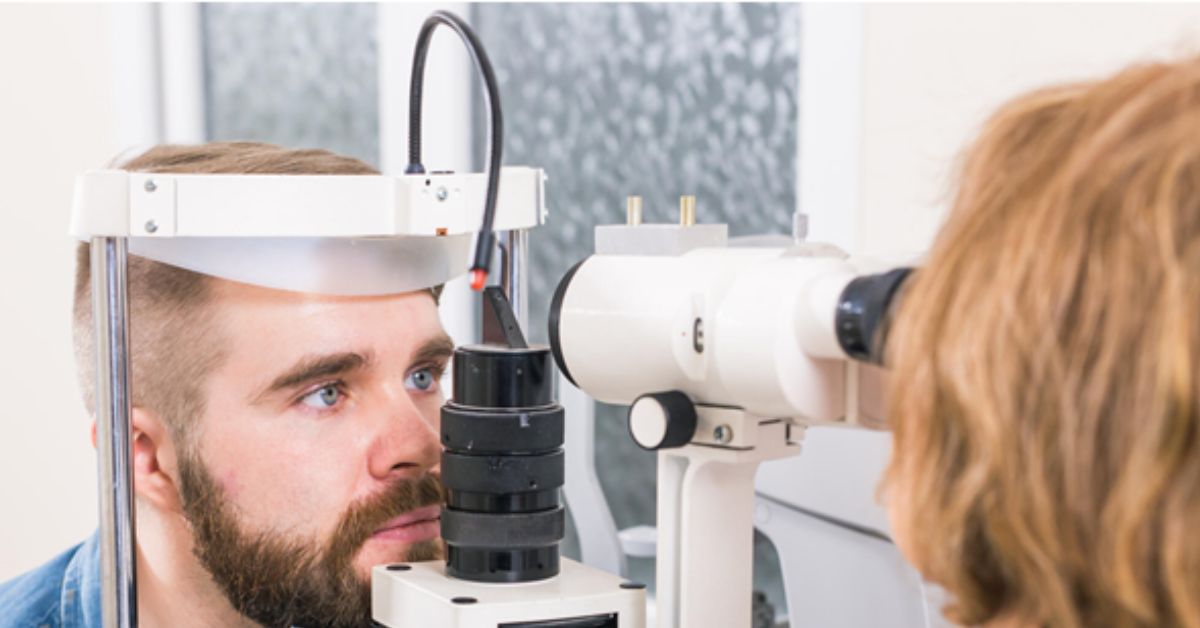
Astigmatism is a common eye problem that can affect anyone, from kids to adults. It happens when the cornea or lens isn’t shaped quite right, leading to blurry vision no matter how far away something is. The good news? It can be fixed with glasses, contact lenses, or surgery. But if kids don’t get treated, it might cause issues later in life.
Let’s dive into how untreated childhood astigmatism can affect young ones as they grow up and why it’s super important to tackle it early!
Amblyopia (Lazy Eye)
Amblyopia, also known as “lazy eye“, is a condition where the brain ignores signals from one eye due to poor vision. It can occur if astigmatism is left untreated in childhood.
Effect on Daily Life
A lazy eye can affect daily life in many ways. For example, it can lead to poor depth perception, which makes it hard to judge how far away things are. This can be especially tough when trying to play sports that need good hand-eye coordination, like basketball or tennis.
Strabismus (Crossed Eyes)
Strabismus is a condition where the eyes do not line up correctly, which can make them look crossed. This issue can arise if a child has astigmatism that isn’t treated.
Effect on Daily Life
In addition to possible cosmetic issues, strabismus can create problems with depth perception, similar to amblyopia. This difficulty might make it hard to do activities like reading or working on a computer for a long time.
Such challenges can also result in eye strain, headaches, and double vision, which can affect daily life. It’s important to understand these effects, as they can impact how we see the world and perform everyday tasks. Seeking help from an eye care professional can lead to better ways to manage these symptoms.
Reduced Quality of Life
Aside from the specific visual complications that can arise, untreated childhood astigmatism can have a significant impact on overall quality of life. Here’s how:
Academic Performance
Children who have untreated astigmatism might find it hard to see the board or read their school materials. This vision problem can make it tough for them to keep up in class, which can lead to lower grades and academic performance.
As their performance declines, it can also hurt their self-confidence. When children don’t feel good about themselves in school, it can impact their future educational and career opportunities. Ensuring that children receive proper eye care is crucial for their success both now and later in life.
Career Limitations
In adulthood, untreated astigmatism can affect job options. For example, people with significant astigmatism might not qualify for careers that need great vision.
This includes professions like pilots and surgeons, where clear sight is crucial. As a result, individuals may have fewer opportunities in these fields, impacting their career paths.
Emotional Well-being
Living with uncorrected astigmatism can affect a person’s emotional well-being. It can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and even depression. This happens because people with this condition often have to deal with a constant struggle to see clearly.
Blurred vision can make everyday tasks challenging, which adds to their stress. Over time, this ongoing difficulty can take a serious toll on how they feel emotionally. It’s important to recognize these challenges and seek help if needed.
Persistent Blurry or Distorted Vision
Without proper treatment, childhood astigmatism can persist into adulthood. This means that individuals may have to live with distorted or blurred vision for their entire lives.
Impact on Daily Activities
Uncorrected astigmatism can make everyday activities challenging and uncomfortable. It can be difficult to drive, read, watch TV, or engage in hobbies without experiencing visual strain or discomfort.
Risk of Other Eye Conditions
If astigmatism is not treated over a long period, it can lead to other eye problems. These include conditions like cataracts and glaucoma.
Cataracts cloud the lens of the eye. Meanwhile, glaucoma can damage the optic nerve. It’s important to address astigmatism to help reduce the risk of these serious issues.
Eye Strain and Headaches
Uncorrected astigmatism can cause significant eye strain and headaches, especially when performing visually demanding tasks. This is due to the constant effort the eyes must put in to compensate for the refractive error.
Impact on Work Productivity
Eye strain and headaches can significantly impact how well you work. When your eyes are tired and you have a headache, it becomes difficult to focus and accomplish tasks. This can lead to lower productivity, meaning you might not get as much done as you could.
Reduced Visual Acuity
Over time, untreated childhood astigmatism can lead to a decline in overall visual acuity. This means that even with corrective lenses or surgery, individuals may never achieve perfect vision.
Impact on Daily Life
Reduced visual acuity can make it challenging to perform everyday tasks and activities that require good eyesight. It can also increase the risk of accidents and injuries in daily life.
Treatment Options
Early detection and treatment of childhood astigmatism can prevent or minimize the potential long-term impacts discussed above. Treatment options include:
Prescription Eyeglasses
Prescription eyeglasses are an effective and non-invasive treatment option for astigmatism. They work by correcting the refractive error, allowing light to focus properly on the retina.
Glasses are effective for mild to moderate astigmatism and can be prescribed even at a young age. They are safe and easy to use, making them ideal for children.
Contact Lenses
Eye contact lenses, particularly toric lenses, are specially designed to correct astigmatism by compensating for the cornea’s irregular shape. These lenses can provide a wider field of vision and may be preferable for older children or teens who are comfortable with them. early intervention
Contact lenses offer clear vision and are more convenient for active children who may find glasses cumbersome during sports or outdoor activities. They need proper care and hygiene to avoid eye infections.
Orthokeratology (Ortho-K)
Orthokeratology is a non-surgical approach that uses rigid gas-permeable contact lenses to reshape the cornea while sleeping. This results in temporary corrected vision without the need for glasses or contacts during the day. Ortho-K is an effective treatment option for children whose parents may have concerns about surgery or their child’s ability to take care of contact lenses.
Laser Eye Surgery (LASIK or PRK)
Laser eye surgery reshapes the cornea to correct astigmatism permanently. LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis) is the most common procedure, while PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy) is another option where the surface of the cornea is reshaped.
LASIK or PRK is typically reserved for adults, but it may be considered for older teens whose eyes have stopped growing and whose vision has stabilized. It provides a long-term solution to astigmatism and eliminates the need for glasses or contact lenses.
Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE)
Refractive Lens Exchange is a surgical procedure where the natural lens of the eye is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) to correct refractive errors like astigmatism. It may be recommended for patients with high levels of astigmatism and those who are not suitable candidates for laser surgery.
Vision Therapy
Vision therapy is a non-surgical approach that involves exercises and techniques to improve visual abilities. This includes focusing, eye teaming, and tracking. It may be recommended in addition to wearing corrective lenses for children with amblyopia or strabismus.
Surgical Options for Severe Astigmatism
For severe astigmatism, surgical options such as corneal transplantation or implantable lenses may be considered. These are more invasive procedures and are often reserved as a last resort.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The best treatment option for each individual depends on various factors. This includes:
Age
Certain treatment options, such as LASIK or RLE, may not be suitable for children. It’s essential to consider their age and potential risks before deciding on a course of action.
Severity of Astigmatism
The severity of astigmatism can also affect the choice of treatment. For mild cases, glasses or contacts may be sufficient, while more severe cases may require surgical intervention.
Personal Preference
Personal preference should also be considered when choosing a treatment option, especially for older children and teens. It’s important to discuss the available options with your child and involve them in the decision-making process.
Maturity Level
For children, their maturity level and ability to handle glasses or contact lenses should be taken into account. This may influence the chosen treatment option.
Medical Professional’s Recommendation
Ultimately, the recommendation of a trained medical professional should be considered when deciding on a treatment option. They can assess various factors and determine the most suitable course of action for your child.
Discover the Long-Term Effects of Childhood Astigmatism
Untreated childhood astigmatism can have long-term impacts on an individual’s vision and overall quality of life. However, with early detection and appropriate treatment, these complications can be avoided or minimized.
It’s essential to prioritize regular eye exams for children and seek professional help if any vision problems are suspected. Remember, treating astigmatism in childhood can pave the way for a bright future with clear vision!
Is this article helpful? Keep reading our blog for more.
HEALTH
Bin Matcha: The Premium Green Tea Power for Daily Health

Introduction to Bin Matcha and its Origins
Are you ready to elevate your daily health routine? Meet Bin Matcha, an exquisite form of green tea that’s taking the wellness world by storm. With its vibrant green color and rich flavor profile, Bin Matcha isn’t just a treat for the senses; it’s packed with incredible health benefits too. Originating from Japan, this premium matcha is not your average cup of tea. It’s a powerful ally in your quest for balance and vitality. Dive into the world of Bin Matcha and discover why you should make it a staple in your life!
What is Matcha and its Benefits?
Matcha is a powdered green tea produced from carefully grown leaves, allowing you to consume the whole leaf rather than just an infused extract. This unique preparation method retains all its nutrients.
Rich in antioxidants, matcha boosts your metabolism and enhances fat burning. It also provides a calm alertness due to its combination of caffeine and L-theanine. This amino acid promotes relaxation without drowsiness.
Moreover, matcha supports heart health by lowering cholesterol levels and reducing blood pressure. Regular intake may support balanced blood sugar levels.
Incorporating matcha into your routine is an easy way to elevate your wellness journey while enjoying its distinct flavor profile—from creamy lattes to vibrant smoothies. The versatility makes it popular among health enthusiasts everywhere!
The Origins of Bin Matcha
Bin Matcha traces its roots back to the ancient tea gardens of Japan. The meticulous cultivation process began centuries ago, with farmers perfecting their techniques over generations.
This premium matcha is derived from shade-grown tea leaves, which are carefully hand-picked during peak harvest seasons. The focus on quality sets Bin Matcha apart, as only the youngest and most vibrant leaves are selected.
Once harvested, these leaves undergo a unique stone grinding process that preserves their delicate flavors and nutrients. This artisanal method enhances the overall character of Bin Matcha, providing an exquisite taste profile that reflects its heritage.
The commitment to sustainability and traditional practices further distinguishes Bin Matcha from mass-produced variants. Each sip carries not just flavor but also a rich history steeped in Japanese culture and dedication to excellence.
What Sets Bin Matcha Apart from Other Green Teas?
Bin Matcha stands out among green teas due to its unique production process. Unlike traditional green tea, where the leaves are steeped and discarded, Bin Matcha uses whole ground leaves. This means you consume the entire leaf, maximizing nutrient intake.
The shade-grown cultivation method enhances its flavor profile. By blocking sunlight before harvest, the plant produces more chlorophyll and amino acids. This results in a vibrant color and a sweeter taste compared to other varieties.
Furthermore, Bin Matcha is meticulously sourced from specific regions known for their ideal growing conditions. The careful selection of these locations ensures high-quality leaves with rich antioxidants.
Bin Matcha offers a smooth texture that sets it apart from coarser green teas. Its fine powder form allows for versatile use in drinks and recipes alike, making it an exciting addition to any health-conscious kitchen.
Health Benefits of Bin Matcha
Bin matcha is more than just a tasty beverage; it’s a powerhouse of health benefits. Packed with antioxidants, it fights free radicals that can damage your cells and lead to chronic diseases.
This premium green tea also boosts metabolism. Drinking bin matcha may help you burn calories more efficiently throughout the day. It’s an excellent choice for those looking to maintain or lose weight naturally.
Additionally, bin matcha promotes relaxation without drowsiness due to its unique amino acid called L-theanine. This compound enhances focus while reducing stress levels, making it perfect for busy days.
Heart health is another benefit associated with this vibrant green powder. Regular consumption may lower cholesterol levels and improve overall cardiovascular function.
With all these advantages, incorporating bin matcha into your daily routine can support your wellness journey in multiple ways.
Incorporating Bin Matcha into Your Daily Routine
Adding Bin Matcha to your daily routine is simple and rewarding. Start your day with a warm cup of matcha tea. Just whisk one teaspoon of Bin Matcha powder into hot water for a refreshing boost.
For those busy mornings, try blending it into smoothies. The vibrant green color adds an appealing touch while enhancing the nutritional value.
Baking enthusiasts can incorporate Bin Matcha’s into their favorite recipes. Muffins or cookies made with this premium green tea not only look great but provide added health benefits too.
Consider sprinkling some on yogurt or oatmeal for breakfast. It’s an easy way to infuse your meals with antioxidants and flavor without much effort.
Even in savory dishes, Bin Matcha’s shines through as a unique seasoning for dressings or marinades, offering depth and richness that elevates everyday meals.
Delicious Recipes Using Bin Matcha
Bin Matcha’s opens up a world of culinary creativity. Incorporating it into your recipes can transform ordinary dishes into extraordinary delights.
Start with a classic Bin Matcha’s latte. Simply whisk together one teaspoon of Bin Matcha’s powder, hot water, and your choice of milk for a creamy treat that energizes your mornings.
For something sweet, try making Bin Matcha’s cookies. Blend the green tea powder into cookie dough for an enticing flavor twist. They’ll not only taste good but also look stunning with their vibrant hue.
Feeling adventurous? Experiment with bin matcha’s smoothies by mixing banana, spinach, and almond milk along with the matcha powder. It’s refreshing and packed with nutrients.
Don’t forget about savory options! A sprinkle of bin matcha’s can elevate salad dressings or marinades, adding depth to your favorite meals without overpowering other flavors.
These recipes are just the beginning; let your imagination flow!
Where to Find Quality Bin Matcha
Finding quality Bin Matcha’s can be an exciting journey. Start by exploring specialty tea shops, where knowledgeable staff often curate the finest selections. These local gems typically offer fresh and authentic products.
Online marketplaces are another excellent option. Reputable brands provide detailed information about their sourcing and processing methods, ensuring transparency in quality.
Look for certifications or reviews from other matcha enthusiasts to gauge the authenticity of the product. A strong community often shares their favorites on social media platforms, making it easy to discover trusted sources.
Don’t underestimate farmer’s markets either. Many vendors sell high-quality teas directly from producers, giving you a unique connection to your matcha’s origins.
Consider joining subscription boxes dedicated to premium teas. They frequently feature different varieties of Bin Matcha’s that allow you to explore new flavors without commitment.
Conclusion
Bin Matcha stands out as a premium choice for those seeking the vibrant benefits of green tea. Its unique origins and cultivation methods contribute to its superior quality, offering an experience that is truly unmatched in the world of matcha.
The health perks associated with Bin Matcha’s are compelling, ranging from enhanced energy levels to improved mental clarity. Incorporating this remarkable powder into your daily routine can be both simple and enjoyable. With delicious recipes at your fingertips, whether you’re whipping up a latte or adding it to smoothies, the possibilities are endless.
As more people become aware of its benefits, finding high-quality Bin Matcha’s has never been easier. Look for reputable suppliers who prioritize authenticity and sustainability.
Embracing Bin Matcha’s could be one of the best choices for nurturing your health journey while savoring every sip along the way.
HEALTH
Kinza Herb: Natural Healing, Beauty & Wellness Benefits

Kinza herb, also known as cilantro or coriander, is more than just a garnish on your plate. This vibrant green herb has a rich history and an array of benefits that make it a staple in kitchens around the world. But its magic doesn’t stop at flavor; kinza herb boasts remarkable healing properties and skincare advantages that have been cherished for centuries. Whether you’re looking to enhance your culinary creations or tap into its medicinal potential, kinza herb is worth exploring. Join us as we dive deep into the fascinating world of this versatile plant and uncover how it can elevate both health and beauty in our lives.
History and Origins of Kinza Herb
Kinza herb, commonly known as cilantro or coriander, boasts a rich history that spans thousands of years. Its origins can be traced back to the Mediterranean region and Southwest Asia. Ancient Egyptians valued it for both culinary and medicinal purposes, often associating it with health and vitality.
The name “kinza” itself has roots in various cultures. In Persian, it’s called “kistant,” while in Arabic, it is referred to as “kuzbara.” This reflects its widespread use across different civilizations.
As trade expanded along ancient routes like the Silk Road, kinza made its way into diverse cuisines around the globe. It became popular not just for flavor but also for its therapeutic properties.
Today, kinza remains a staple in many kitchens worldwide, celebrated for its unique taste and numerous health benefits. Its journey through time showcases how this humble herb has influenced food culture across continents.
Medicinal Uses of Kinza Herb
Kinza herb, also known as cilantro or coriander, boasts a rich history in traditional medicine. Its leaves and seeds are packed with phytochemicals that offer various health benefits.
One of the standout features is its anti-inflammatory properties. Kinza can help reduce inflammation in conditions like arthritis and other chronic diseases.
Additionally, it’s praised for its ability to aid digestion. It helps alleviate bloating and gas while promoting healthy gut flora.
This powerful herb is also recognized for its antioxidant effects. These compounds combat oxidative stress, supporting overall well-being.
Moreover, kinza has been linked to lowering cholesterol levels. Regular consumption may contribute to improved heart health over time.
People often use it as a natural remedy for respiratory issues too. The herb may help relieve symptoms associated with colds and allergies by acting as an expectorant.
Benefits for Skin Care
Kinza herb, often celebrated for its culinary uses, also shines in the realm of skincare. Packed with antioxidants and essential oils, it helps combat free radicals that can lead to premature aging.
The herb’s anti-inflammatory properties work wonders on irritated skin. It soothes redness and reduces puffiness, making it a go-to remedy for those struggling with sensitive skin conditions.
Moreover, kinza is known for its antibacterial qualities. This makes it effective in fighting acne-causing bacteria while promoting clearer skin. Many beauty enthusiasts incorporate it into their routines through homemade masks or serums.
Using kinza in your skincare regimen not only nourishes the skin but adds a refreshing glow as well. Its unique scent can elevate your mood too!
Health Benefits of Consuming Kinza Herb
Kinza herb, known for its vibrant flavor, packs a nutritional punch. Rich in vitamins A and C, it supports eye health and boosts the immune system. Consistent intake strengthens immunity and reduces everyday illness risks.
Additionally, kinza is known for its antioxidant properties. They counteract oxidative damage by stabilizing reactive molecules. This may lower the risk of chronic diseases linked to aging.
Moreover, kinza aids digestion. Its natural oils stimulate digestive enzymes, promoting better nutrient absorption and alleviating bloating or discomfort after meals.
This herb also has anti-inflammatory effects that can benefit those dealing with conditions like arthritis or joint pain. Adding kinza to your diet might provide relief from inflammation-related symptoms.
Incorporating kinza into daily meals not only enhances flavor but also offers numerous health advantages worth considering for anyone seeking a healthier lifestyle.
How to Use Kinza Herb in Cooking?
Kinza herb, known for its vibrant flavor and aroma, can elevate any dish. Use it fresh or dried to enhance your culinary creations.
Start by adding chopped kinza to salads for a refreshing twist. It pairs beautifully with tomatoes, cucumbers, and avocados.
For cooking enthusiasts, incorporate kinza into soups or stews. Its essence infuses gradually, offering depth to the broth without overpowering other flavors.
Consider blending kinza into sauces or marinades. This adds an herby kick that complements grilled meats wonderfully.
If you enjoy rice dishes, toss some finely chopped kinza into your pilaf or biryani just before serving. The bright green color will visually attract while enhancing taste.
Experiment by sprinkling it over roasted vegetables as a finishing touch. The warmth of the veggies brings out kinza’s aromatic qualities perfectly.
Precautions and Side Effects
While kinza herb is widely celebrated for its health benefits, it’s important to exercise caution. Some individuals may experience allergic reactions. If you notice any unusual symptoms after consuming kinza, discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should be particularly careful. The effects of kinza on pregnancy are not well-studied, so it’s wise to seek medical advice before incorporating it into your diet.
Additionally, excessive consumption might lead to digestive issues like bloating or gas. Moderation is key when adding any new ingredient to your meals.
People with specific medical conditions should also check with their doctors before using the herb regularly. It’s always better to be safe than sorry when exploring natural remedies like kinza herb.
Conclusion
Kinza herb, also known as coriander or cilantro, is more than just a culinary delight. Its rich history and various medicinal benefits make it an invaluable addition to any diet. From enhancing your skin’s glow to boosting overall health, kinza herb offers a plethora of advantages.
Incorporating kinza into your meals can elevate flavors while providing essential nutrients. Whether you’re adding it fresh to salads or using its seeds in spice blends, the versatility of this herb knows no bounds. However, it’s essential to enjoy it mindfully and be aware of possible side effects.
Embracing kinza herb means embracing wellness and flavor in equal measure. By understanding its uses and benefits, you can harness its potential for both cooking and health enhancement. So next time you reach for that bunch of greens at the store, remember that kinza isn’t just an ingredient; it’s a pathway to better well-being.
HEALTH
Attrities: Causes, Symptoms, and Ways to Improve Quality of Life
Attrities is a term that often surfaces in conversations about joint pain, but its impact goes far beyond mere discomfort. For millions of people, attrities can encroach on daily activities and affect quality of life. Understanding this condition is vital for anyone navigating its challenges or supporting someone who does.
With various types presenting unique hurdles, it’s crucial to recognize the symptoms early and seek appropriate treatment. From lifestyle changes to exercises tailored for relief, there are numerous ways to manage attrities effectively. This blog post will explore the intricacies of attrities: its causes and symptoms, diagnosis options, effective treatments, and supportive therapies designed to enhance well-being.
Whether you’re newly diagnosed or have been living with attrities for years, understanding your path forward can empower you in managing this condition successfully. Let’s delve into what you need to know about living well with arthritis.
Understanding Attrities
Attrities is a complex condition that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation and pain. It can occur in various forms, each with its own characteristics and triggers.
At its core, attrities results from the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy joint tissues or wear and tear over time. This leads to swelling, stiffness, and often significant discomfort.
The prevalence of attrities is staggering; it affects people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds. Understanding this condition begins with recognizing that it’s not just an “older person’s disease.”
Genetics, lifestyle factors like diet and exercise habits, as well as environmental influences can all contribute to developing attrities. Knowing these details helps demystify the challenges faced by those living with this chronic illness.
Types of Attrities and their Causes
Attrities is not just one condition; it encompasses over 100 types. Every form presents distinct causes and features.
Osteoattrities, the most common form, often results from wear and tear on joints over time. Aging plays a significant role here. Joint injuries can also lead to this degenerative condition.
Rheumatoid attrities is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system wrongly targets the joints. Genetics and environmental factors contribute to its onset.
Psoriatic attrities occurs in some individuals with psoriasis, linking skin issues with joint inflammation. The exact cause remains elusive but may involve genetic predisposition.
Gout arises from excess uric acid in the bloodstream, leading to sudden, severe pain usually in the big toe. Dietary choices can influence these levels significantly.
Understanding these different types helps tailor appropriate treatment strategies for those affected by attrities.
Common Symptoms of Attrities
Attrities presents a range of symptoms that can vary from person to person. Joint pain is the most common complaint, often described as a dull ache or sharp sensation during movement.
Swelling around affected joints may also occur. This inflammation can lead to stiffness, making it difficult for individuals to perform everyday tasks.
Another notable symptom is fatigue. Many people with attrities experience tiredness that seems unrelated to their activity level. This overall exhaustion can impact daily life significantly.
Additionally, some might notice changes in joint appearance. Deformities or nodules may develop over time, signaling progression of the condition.
Reduced flexibility is a frequent issue associated with attrities. People often find they cannot bend or stretch their joints fully without discomfort, limiting mobility and independence in activities.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing attrities involves a thorough examination of your medical history and physical condition. Healthcare providers often perform blood tests and imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRIs, to determine the type and severity of the disease.
Once diagnosed, treatment options vary widely based on the specific type of attrities you have. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation. For some patients, corticosteroids may be recommended to suppress immune responses.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can help slow disease progression in inflammatory types like rheumatoid attrities. Physical therapy is also beneficial for improving joint function.
In serious cases, surgery may be required to restore or replace affected joints. It’s crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor treatments that suit individual needs for optimal management of attrities symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Quality of Life
Making small lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on your quality of life when dealing with attrities. Start by focusing on nutrition. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation.
Staying hydrated is equally important. Water aids joint lubrication and overall bodily functions. Aim to drink enough water daily to keep your body functioning optimally.
Sleep also plays a crucial role in managing attrities symptoms. Establishing a consistent sleep routine enhances rejuvenation and reduces fatigue.
Incorporating stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga can improve mental well-being too. These practices not only calm the mind but may also alleviate physical tension caused by stress.
Setting realistic goals for activity levels encourages movement without overwhelming yourself. Gentle activities promote mobility while respecting your body’s limits, empowering you to take control of your journey with attrities.
Exercises for Attrities Relief
Exercise plays a vital role in managing attrities symptoms. It helps to maintain mobility and reduce stiffness. Even gentle movements can make a significant difference.
Low-impact activities are ideal for those dealing with attrities. Swimming and cycling provide excellent cardiovascular benefits without putting pressure on the joints. These exercises keep the body active while minimizing discomfort.
Stretching is essential too. Simple stretches can enhance flexibility and range of motion, making daily tasks easier. Consider incorporating yoga or tai chi into your routine; they promote balance alongside relaxation.
Strength training should not be overlooked either. Building muscle around affected joints provides extra support, which may help alleviate pain over time. Using resistance bands or light weights is an effective way to start safely.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any new exercise program tailored specifically for your needs and abilities will yield the best results in your journey toward better health.
Alternative Therapies for Managing Attrities Pain
Alternative therapies can offer relief for those managing attrities pain. Many individuals find comfort in practices like acupuncture, which involves inserting thin needles at specific points on the body to promote healing and reduce discomfort.
Herbal remedies are another popular option. Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound known for its anti-inflammatory effects. Incorporating it into your diet may help alleviate symptoms.
Practices that connect mind and body, like yoga and meditation, may also offer benefits. These practices not only improve flexibility but also foster relaxation, helping to combat stress that often exacerbates pain.
Essential oils like peppermint or lavender may provide soothing effects when used in massages or diffusers. The aroma can create a calming environment while potentially easing muscle tension.
Before trying any alternative therapy, consulting with a healthcare professional is wise to ensure safety and compatibility with existing treatments.
Coping with Emotional Effects of Attrities
Living with attrities can take a toll on emotional well-being. Chronic pain and fatigue often lead to feelings of frustration and sadness.
It’s essential to acknowledge these emotions. You’re not alone in what you feel. Many people experience similar challenges, which can help create a sense of connection.
Finding healthy coping mechanisms is crucial. Consider journaling your thoughts or engaging in creative activities like painting or knitting. These outlets can provide relief and distraction from daily discomforts.
Mindfulness practices, such as yoga or meditation, may also be beneficial. They encourage relaxation and foster a positive mindset.
Talking to friends, family, or support groups about your experiences can ease the burden too. Sharing your story creates understanding and allows for mutual support during tough times.
Remember that seeking professional help is always an option if feelings become overwhelming. Mental health matters just as much as physical health when managing attritieseffectively.
Support Systems for Attrities Patients
Support systems play a crucial role in managing attrities. They provide emotional strength and practical assistance when needed most.
Family and friends can be invaluable resources. Their understanding and encouragement help ease feelings of isolation often experienced by those living with chronic pain. Simple gestures, like cooking a meal or offering to run errands, make a significant impact.
Joining support groups is another excellent way to connect with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences fosters camaraderie and provides insights into coping strategies that work for different individuals.
Online forums also offer valuable connections without geographical limitations. Patients can seek advice, share stories, and even find motivation through digital communities.
Healthcare professionals should not be overlooked as part of the support system. Regular check-ins with doctors or physical therapists ensure tailored care while addressing concerns about medication or exercise routines effectively.
Conclusion
Attrities is a multifaceted disorder impacting millions of individuals around the globe. It’s not just an old person’s ailment; it can strike at any age and significantly impact daily life. Understanding the various types of arthritis, their causes, and symptoms is crucial for effective management.
Treatment options vary widely from medications to physical therapies. Each individual’s needs are unique, so personalized care plans are essential for improving quality of life. Lifestyle changes like diet modifications and regular exercise play a significant role in managing attrities symptoms.
For those seeking relief beyond traditional methods, alternative therapies such as acupuncture or massage can offer additional support. Emotional well-being should also be a priority; it’s important to acknowledge the psychological toll attrities can take on individuals and their families.
Fostering connections with support groups or communities dedicated to attrities can provide invaluable encouragement and advice through shared experiences. Embracing these strategies will help many navigate the challenges posed by this chronic condition more effectively while enhancing overall well-being.

 HOME IMPROVEMENT11 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT11 months agoThe Do’s and Don’ts of Renting Rubbish Bins for Your Next Renovation

 BUSINESS12 months ago
BUSINESS12 months agoExploring the Benefits of Commercial Printing

 BUSINESS12 months ago
BUSINESS12 months agoBrand Visibility with Imprint Now and Custom Poly Mailers

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoThe Surprising Benefits of Weight Loss Peptides You Need to Know

 HEALTH7 months ago
HEALTH7 months agoYour Guide to Shedding Pounds in the Digital Age

 TECHNOLOGY10 months ago
TECHNOLOGY10 months agoDizipal 608: The Tech Revolution Redefined

 HOME IMPROVEMENT7 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT7 months agoGet Your Grout to Gleam With These Easy-To-Follow Tips

 HEALTH11 months ago
HEALTH11 months agoHappy Hippo Kratom Reviews: Read Before You Buy!












