Uncategorized
Customer Journey Mapping Guide: Understanding, Implementing, & Improving Experiences
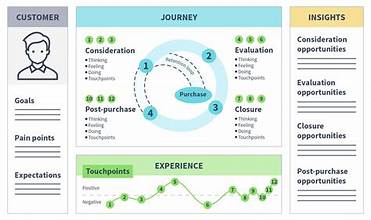
The customer journey from first contact to final sale is seldom linear. Customers interact with brands through various touchpoints, often traversing a convoluted path before making a purchase decision. This journey is further complicated by evolving technologies and shifting consumer behaviors. Successful businesses turn to customer journey mapping to navigate this complexity and enhance customer experiences.
What is Customer Journey Mapping?
Creating a customer journey map is visualizing customers’ processes, needs, and perceptions throughout their interactions with an organization. It helps grasp both seen and unseen steps customers take when engaging with your business. This process allows you to:
1. Gain insights: Understand existing customer journeys better.
2. Assess impact: Optimize budgets and efforts for enhancing customer experiences.
3. Identify issues/opportunities: Diagnose current customer journey challenges.
4. Foster innovation: Explore avenues for transforming customer experiences.
A customer journey map delves deeper into understanding customers, going beyond surface interactions with the brand. It prompts consideration of unseen aspects, crucial for shaping the overall experience. When mapping the journey, focus on pivotal moments of emotional significance. For instance, in car purchasing, the emotional peak occurs when picking up the car after selecting the color and model.
Aligning these moments with customer expectations is vital for achieving business objectives. This requires a comprehensive understanding of the customer journey, their thoughts, and needs at each stage. By developing a customer journey map, businesses can empathize with customers, enhancing their understanding and improving their experiences.
Types of Customer Journey Maps
The customer journey can be mapped in as many ways as there are customers. Organizations often opt for a tailored approach to customer journey mapping that aligns with their unique experiences. Nonetheless, most customer journey maps fall into four distinct categories:
1. Current state
Current state journey maps are widely used, illustrating the actions and emotions customers undergo as they progress through the existing funnel. They rely on reliable data and provide insights into the current status of customer experiences. Regular use of these maps facilitates ongoing refinement and enhancement.
2. Day in the life
Offering a broader perspective beyond direct interactions with the business, a day-in-the-life customer journey map considers all the thoughts, actions, and emotions a potential customer might encounter throughout their day. This proactive approach aids in exploring new market strategies and addressing customer needs, including unaddressed pain points in traditional mapping.
3. Future State
The future state customer journey map looks ahead, envisioning the thoughts, actions, and emotions customers will experience in future interactions with the business. It is instrumental in creating novel customer experiences rather than simply modifying existing ones. While innovation and creativity drive this approach, insights from current-state journey maps inform the foundation for ideal future-state maps.
4. Service blueprint
A service blueprint customer journey map serves as a simplified version of current-state, future-state, or day-in-the-life CJMs. These blueprints focus on specific aspects of the customer journey, such as people or processes, and provide guidance on the necessary actions to steer customers in the intended direction. They are invaluable tools for defining and refining the customer experience.
IMPORTANCE OF CUSTOMER JOURNEY MAPPING
1. Identifying Challenges: Pinpoint critical customer pain points for targeted solutions.
2. Boosting Loyalty: Craft personalized journeys to enhance satisfaction and retention.
3. Refining Strategies: Use insights to optimize marketing and sales efforts for better outcomes.
4. Enhancing Collaboration: Foster teamwork across departments for cohesive customer experiences.
5. Spotting Deficiencies: Identify gaps in customer service management and communication channels for proactive improvement.
6. Customer-Centric Approach: Prioritize customer needs to drive satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map
Creating a Customer Journey Map (CJM) involves six fundamental steps. As mentioned earlier, each customer journey is unique, meaning that your approach to creating a CJM may vary from the one outlined here. To achieve optimal results, follow these steps as a starting point and adjust your map accordingly to better cater to your buyers’ needs.
1. Define Buyer Personas
To effectively guide your customers, you must first understand who they are. Develop multiple buyer personas to accommodate customers entering the funnel at different stages. These personas should provide detailed descriptions of key customers, their needs, and their interactions with your brand.
2. Grasp Customer Goals
With personas established, the next step is to consider the various paths and channels your customers may take and the activities and touchpoints involved in their journey. This will help you clarify your customers’ goals. This stage may involve thorough research, such as analyzing customer feedback, studying emails and support transcripts, and utilizing customer analytics tools. Once you understand your customers’ goals, apply them to each stage of the journey on your CJM.
3. Identify and Map Touchpoints
Ideally, the touchpoints your customers encounter should address their concerns, answer their questions, and guide them toward making a purchase. These touchpoints encompass any interaction the customer has with your brand across all channels and at any point in their journey, including post-purchase. Customer feedback can help generate touchpoints, or visualizing the journey from the customer’s perspective may offer insight into interactions and timing.
4. Assess the Journey
With your map complete and the customer journey visualized, it’s time to assess the overall picture. Determine where the journey is effective and optimal, and identify any gaps or issues that may hinder or divert customers. This involves reviewing customer goals, identifying areas of friction, and examining abandoned purchases and their contributing factors.
5. Prioritize Solutions
Not all issues with the customer journey are equally critical. Some friction points may be minor, while others could significantly undermine your marketing and sales efforts. Prioritize addressing the issues with the greatest potential for improvement. Additionally, ensure that each touchpoint contributes to guiding customers through the funnel toward the desired goal.
6. Continuously Revise and Enhance
Customers, companies, and their journeys are not static. Nearly every aspect of your CJM reflects a dynamic aspect of your business. Therefore, it’s essential to continually refine your CJM through regular testing, revisions, and evaluations. Revisit your customer journey map at least twice a year or whenever you make changes to your product offering or business processes to ensure its accuracy and usefulness in depicting how customers interact with your brand.
Conclusion
The comprehensive manual on customer journey mapping sheds light on customers’ intricate paths from initial contact to final purchase. By visualizing these journeys, businesses obtain invaluable insights into customer experiences, enabling them to pinpoint pain points, encourage innovation, and improve collaboration across departments.
Organizations can better address customer needs and boost satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue through customized methods such as current state, day in the life, future state, and service blueprint maps. By adhering to the six fundamental steps outlined for creating a customer journey map, businesses can continuously refine and improve their comprehension of customer interactions, ensuring they remain adaptable to changing consumer behaviors and preferences.
Ultimately, customer journey mapping serves as a potent instrument in crafting significant experiences that resonate with customers and drive sustainable business growth in today’s ever-changing marketplace.
Uncategorized
How Real Estate Tokenization Is Changing the Way We Invest in Property

It has always been considered that real estate is a long-term and stable investment. Conventionally, it has involved heavy capital requirement, a lot of paper work, and prolonged holding periods. However, as the blockchain technology is developing, a new approach to investing in property is coming up, namely, the real estate tokenization.
The new method is quickly catching up in the global markets, particularly among new investors, and even experienced players who are looking forward to efficiency, flexibility, and accessibility in property markets. In its essence, real estate tokenization is the process of digitalizing physical property into tokens in a blockchain.
As mentioned in the detailed articles of the Tokenizer.Estate blog, tokenization has introduced new modalities of owning and monetizing property with the absence of the conventional barriers. These are tokens which are shares or fractions of an actual asset. They may be purchased, sold or traded as any other digital asset.
How Real Estate Tokenization Works
The concept of real estate tokenization lies on blockchain, which is a decentralized digital record that guarantees security, transparency, and efficiency. It is done in a number of steps:
- An asset is identified, and an assessment is made regarding a real estate asset.
- The asset is legally designed so as to permit fractional ownership.
- The whole value of the asset is broken into digital tokens.
- These tokens are sold on a blockchain and offered to investors.
The tokens are a part of the property. A token can give an investor income rights (e.g. rental returns), ownership rights or voting rights in property decisions, depending on the structure. The tokens are usually emitted via smart contracts that automate most essential activities including income distribution or transfer of ownership.
Compliance is usually checked by platforms that provide these services through Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks. This combination of regulatory procedures and blockchain infrastructure forms a stable and secure environment of investors.
Key Benefits of Real Estate Tokenization
There are numerous advantages of tokenization that cannot always be found in the traditional real estate investing. So, what are the most powerful ones? Let us take a look:
Fractional Ownership
The most radical advantage is the fractional ownership. Investors can acquire small units of properties in the form of tokens rather than getting a whole property. This brings the barrier of entry to a substantial level where more people can participate even without huge capital.
Liquidity
In conventional real estate, the assets are illiquid since the transaction process takes a long period of time and there are fewer buyers. Using tokenization, assets, however, get more liquid. The holders of tokens have the ability to sell their stocks in the secondary markets, which gives them an exit strategy and the current assessment of their assets.
Accessibility
Real estate is available to investors all over the world in a tokenized form. With the blockchain, the geographical location is no longer a boundary to investment. It is more inclusive as anyone with internet connection and a digital wallet can take part in property investment.
Transparency and Security
The fact that blockchain is transparent implies that all transactions are logged, verifiable and unchangeable. This minimizes frauds, increases confidence, and record keeping. Smart contracts also eliminate human error and automate important actions.
Real Estate Tokenization: Real-World Examples
The real estate tokenization practice is not hypothetical. It is already under implementation in a number of regions of the world. A good example is that of Dubai which has gone to great extents to incorporate blockchain in its property industry.
Dubai introduced a pilot program, according to which land titles could be tokenized. The city made tokenization a part of its legal framework which guaranteed its transparency and legal compliance. The Dubai Land Department and VARA-supported project are anticipated to make a major part of its property market digital and tokenized by 2033.
The other real-world application is a tokenized tiny-home project in Portugal. This project allowed investors worldwide to co-invest in a development along the coastal region in tokens. These illustrations demonstrate that tokenization is already empowering emerging forms of real estate investing, opening up the market and its potentiality.
Comparing Traditional vs. Tokenized Real Estate Investment
| Feature | Traditional Real Estate | Tokenized Real Estate |
| Minimum Investment | High | Low (fractional ownership) |
| Liquidity | Low | High (via token trading) |
| Accessibility | Limited by geography | Global access |
| Transaction Time | Weeks or months | Minutes or hours |
| Regulatory Transparency | Often complex | Built-in via blockchain |
| Ownership Structure | Full or joint ownership | Programmable via smart contracts |
Why This Matters to Investors
Tokenization is not just a technology fad. It is a true change in the mindset of people with regard to property as an investment. To new investors it implies more access and less risk. It provides efficiency in operations and flexibility in portfolio to the institutions. The market of tokenized real estate will rise by a large margin as governments and legal systems start to adjust to the new reality.
Nevertheless, it is a developing area. Regulations are regionally different and adoption of technology is not even. Because of this they should learn before jumping in as a potential investor. Tokenizer.Estate is one of the most popular sites that provide the information, case studies and legal background to those who are interested in this field.
Its blog does not only discuss the basics but also touches upon the ways, in which various regions are adjusting to tokenization, which provides a good source of information to both novice and experienced investors.
The Road Ahead
With the growth of adoption, we will see the tokenization of the commercial and residential property markets redesign both. Blockchain has the potential to enhance efficiency and accessibility of property investments in smart cities, cross-border investments, and digital real estate funds.
It is also possible to witness further government partnerships which preconditions mainstream integration. However, there are legal recognition issues, tax issues, and long-term token valuation that must be resolved. The education will play a significant role in making both the investors and the regulators proceed with wisdom.
Conclusion
The tokenization of real estate is already transforming the realm of investing. With fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity to international access, it is an attractive alternative to the conventional models. This technology may become the norm in the portfolio of property investors across the globe as more case studies are released and legal frameworks are established.
To learn more on these concepts, regional trends and success stories in real life, visit the Tokenizer.Estate blog. It gives a closer look at the process of tokenization and its implications on the future of real estate.
Uncategorized
Meet AINMHÍ: The Award-Winning Irish Skincare Brand Redefining Natural Beauty

Over the past few years, the population has become increasingly concerned with what they apply on their skin. The need of natural yet effective skincare is on the rise. One of the new stars in this genre is a brand that is based in the west coast of Ireland. AINMHÍ is a female-owned skincare brand that introduces the ancient wisdom of the Celtic plants into the contemporary skincare practices.
What Makes AINMHÍ Different
Animal (or spirit) in Irish Gaelic is AINMHÍ (pronounced “an-vee”). This name shows the strong relation of the brand with nature and wild Irish landscapes. Their products are all produced in small batches in Kenmare; a town on the Wild Atlantic Way in Ireland. Wild-harvested and organic ingredients such as flax oil, seaweed, self-heal flower and spring water are used in the brand. These are perfectly mixed with the newest skincare science to produce products that are mild, efficient, and deeply traditional.
AINMHÍ is not based on artificial perfumes and synthetics chemicals like many commercial brands. No ingredient is used without a reason, and every formula is provided to help with both skin and emotional health. This peculiar combination of nature and science has made AINMHý find a fan base both in Ireland and worldwide.
The Woman Behind the Brand
Sarah, an Irish chemist with a passion of plants and holistic health, started AINMHÍ. Having spent time in the beauty industry, she desired to do something new, something that will reflect the land, the people, and the healing effects of the plants and this was how she came up with the idea of a skincare line. Sarah personally crafts each of her products and ensures that each bottle contains not only skincare products, but also a feeling of relaxation and attention.
She also collaborates with local foragers and small farms to get the best Irish ingredients. The company is self-governing and highly committed to sustainability, ethics and community. All products are pH balanced, cruelty-free and skin-compatible tested in an Irish laboratory.
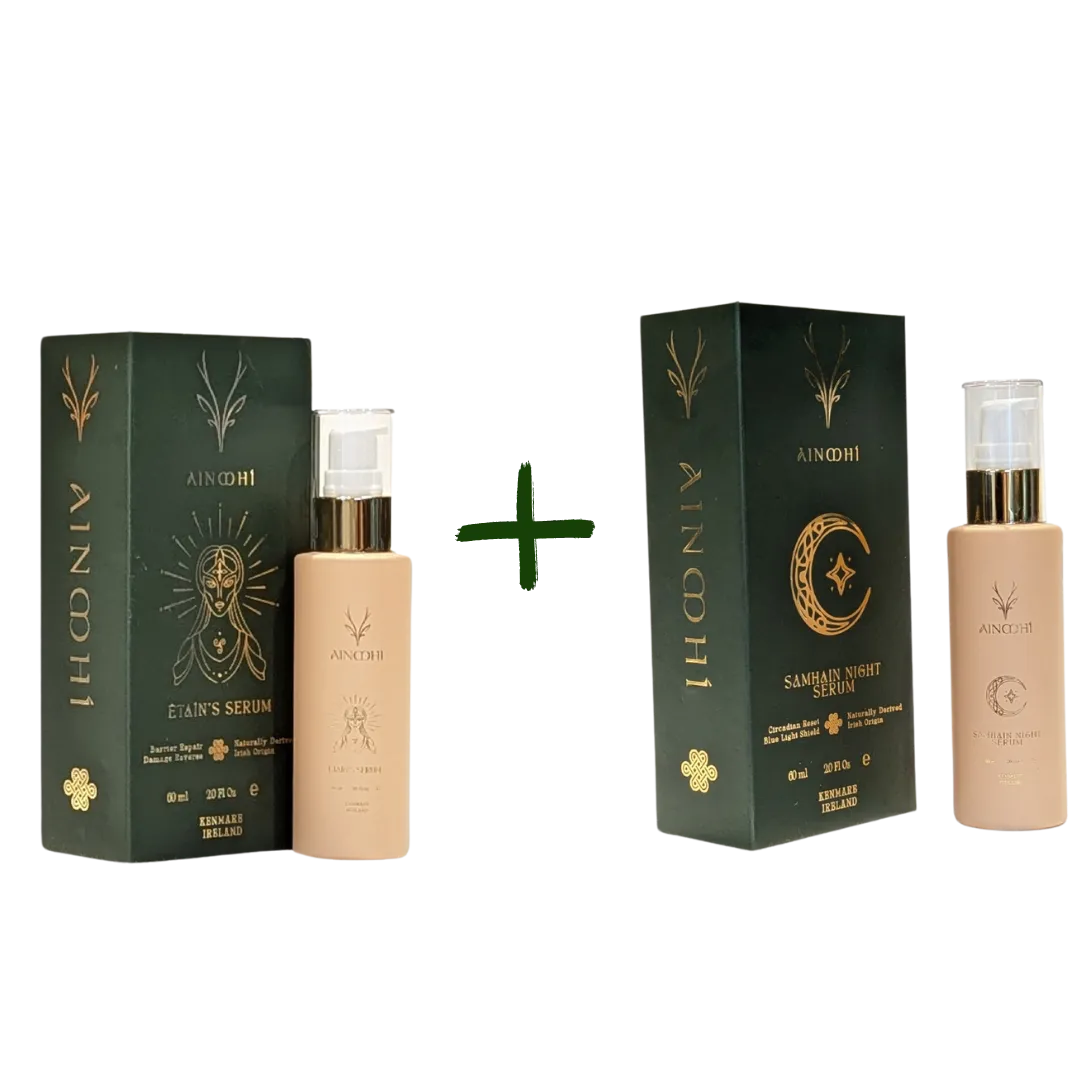
Spotlight on Hidden Solstice Serum
The Hidden Solstice Serum is one of the award-winning products of the brand and one of the most popular products of the brand. The serum is based on the ancient Celtic summer solstice rituals and is meant to replicate the effect of the sunlight on the skin. It has an exclusive ingredient that is known as Great Burnet that enables the skin to produce more Vitamin D and serotonin. This will make the skin look bright and healthy as well as can lift your mood.
Other strong botanicals that are mixed in the Hidden Solstice Serum also include flax oil, Irish sage, self-heal flower, Spirulina and spring water. The combination of these ingredients helps to moisturise the skin, reduce redness and maintain the natural barrier on the skin. The common feedback of the users is that their skin is softer, more even, and less likely to break out and become irritated.
Benefits of Choosing AINMHÍ Skincare
By selecting AINMHÍ, you do not purchase only skincare. You are patronizing a company that is passionate about quality, tradition, and nature. Following are some reasons why this brand is so popular with customers:
- Crafted in Ireland with Irish produce
- Sulfate-free, parabens-free, and free of artificial fragrances
- Suitable to sensitive and reactive skin types
- PH neutral and animal friendly
- Promotes emotional health by using aromatherapeutic formulas
- Real results supported by award winning formulas
The benefits also make AINMHÍ stand out in a crowded market, particularly those interested in skincare as clean and honest as it is effective.
Global Recognition and Awards
AINMHÍ has already left its trace on the global arena. The Hidden Solstice Serum was awarded Best Serum 2025 in the UK and Ireland, among the established brands in the clean beauty industry. The awareness has been used to expose the brand to new markets seeking quality, nature based skin care products.
The customers all over Europe and even outside of it often review the relaxing textures, relaxing fragrances, and the visible skin changes. People say that it is like introducing a little Irish nature to their everyday self-care routine.
A Skincare Ritual Inspired by the Celtic Calendar
The other distinct thing about AINMHÍ is that it makes use of Celtic Wheel of the Year. All the products are associated with one of the ancient seasonal celebrations like Samhain, Imbolc, Beltane, and Lughnasadh. This adds more meaning to every piece and invites users to relate to the rhythms of nature.
The ceremonies associated with these festivals are not supposed to be a mere skin care. They encourage individuals to take their time, be in the moment and practice self-care holistically. This does not only make the AINMHÍ experience a beauty experience, but wellness and mindfulness as well.
A Growing Community of Supporters
With the help of great word-of-mouth, positive reviews, and community, AINMHÍ keeps expanding. The brand regularly publishes tips about Celtic traditions, botanic advantages and seasonal rituals on its blog and social media. Customers get a sense that they are involved in something bigger than a simple purchase, they even join a wellness movement based on the feeling of respect towards nature and themselves.
This feeling of association has made the brand grow outside Ireland and serve customers in Europe, the UK and North America. With every release of new products, AINMHÍ has had a tendency to mix the old and the new in such a manner that has seemed new, deliberate, and actually effective.
Conclusion
AINMHÍ is not a regular skincare brand. It is an award-winning, mindful practice of natural beauty, which is inspired by the rich traditions and healing nature of Ireland. Whether it is the handcrafted formulas, the wild-harvested ingredients and seasonal inspirations, each aspect is carefully selected. With more individuals searching out clean, sustainable, and soul-enriching skincare, AINMHÍ is a brand to be discovered and depended on.
Uncategorized
Why Internal Medicine Specialities and Primary Care in Coachella Are the Future of Adult Healthcare
Healthcare today is evolving to meet the growing and diverse needs of adult patients. With rising chronic conditions, preventive health concerns, and the need for consistent follow-up, both primary care in Coachella and internal medicine specialities play a vital role in delivering high-quality, long-term care.This article explores how these two aspects of adult medicine complement each other, what services they provide, and why patients in Coachella and surrounding areas are increasingly choosing this combination for comprehensive healthcare.
The Foundation: Primary Care and Its Importance in Community HealthWhat Is Primary Care?Primary care serves as the first point of contact for patients seeking medical attention. It covers general wellness, acute illness, chronic disease management, and preventive screenings. Primary care physicians often build lasting relationships with patients, making them an essential part of lifelong health planning.Services Typically Offered in Primary Care
General health assessmentsDiagnosis and treatment of common illnessesPreventive screenings and vaccinationsChronic disease monitoring (e.g., diabetes, hypertension)Health education and lifestyle counseling
Diving Deeper: What Are Internal Medicine Specialities?Understanding Internal MedicineInternal medicine is a medical field focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases in adults. Internists are experts in handling complex cases involving multiple conditions, often working behind the scenes to solve diagnostic puzzles and manage long-term care.A Closer Look at Internal Medicine SpecialitiesInternal medicine encompasses several sub-disciplines that allow internists to focus on specific systems or conditions. These include:
Cardiology (heart and blood vessels)Endocrinology (hormonal and metabolic disorders)Pulmonology (lungs and respiratory system)Gastroenterology (digestive system)Rheumatology (joints and autoimmune disorders)Nephrology (kidneys)Infectious DiseaseHematology and Oncology
The Synergy Between Primary Care and Internal MedicineCoordinated and Comprehensive CareWhen primary care providers work closely with internal medicine specialists, patients benefit from:
Seamless referrals and follow-upsCoordinated treatment for chronic or multi-system conditionsTimely screenings and early detectionPersonalized health plans backed by deep diagnostic insight
Better outcomes due to early interventionLower healthcare costs through preventionHigher satisfaction with continuity and trust in careTailored treatment for complex conditions
When Should Adults Seek These Services?Situations That Call for Primary Care
Annual physicals and wellness visitsNew or ongoing non-emergency symptomsPreventive screenings and lifestyle adviceVaccination updates
Complex or chronic conditions requiring expert evaluationMulti-organ system involvementUnresolved or undiagnosed symptomsNeed for disease-specific monitoring (e.g., diabetes, heart disease)
Why Choose Indus Medical Associates?Indus Medical Associates combines the best of both worlds: trusted primary care in Coachella and a full spectrum of internal medicine specialities. Their board-certified team offers compassionate care rooted in medical expertise, serving individuals with dedication and personalized attention.
Final Thoughts: Invest in Long-Term, Specialized CareHealth is not just about curing illness—it’s about maintaining balance, detecting risk early, and building a lifelong relationship with knowledgeable healthcare professionals. By combining the localized benefits of primary care in Coachella with the depth of internal medicine specialities, patients receive the well-rounded care they deserve.Choose the care that’s committed to your future. Choose smart. Choose comprehensive. Choose Indus Medical Associates.

 TECHNOLOGY4 months ago
TECHNOLOGY4 months agoBlog Arcy Art: Where Architecture Meets Art

 ENTERTAINMENT2 weeks ago
ENTERTAINMENT2 weeks agoExploring the Kristen Archives: A Treasure Trove of Erotica and More

 LIFESTYLE4 months ago
LIFESTYLE4 months agoThe Disciplinary Wives Club: Spanking for Love, Not Punishment

 LIFESTYLE2 weeks ago
LIFESTYLE2 weeks agoWho Is Sandra Orlow?

 GENERAL3 days ago
GENERAL3 days ago5 Factors That Affect Tattoo Removal Success

 ENTERTAINMENT8 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT8 months agoYuppow: Your Free Source for Movies and TV Shows

 ENTERTAINMENT1 week ago
ENTERTAINMENT1 week agoKiss KH: The Streaming Platform Redefining Digital Engagement and Cultural Currents

 HOME IMPROVEMENT5 days ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT5 days agoGet Your Grout to Gleam With These Easy-To-Follow Tips