HEALTH
The Revolutionary Treatment Using Ketamine for OCD

Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) can be relentless. They struggle with intrusive thoughts.
They also feel an urgent need to repeat rituals. This brings a life of intense anxiety. There are brief moments of relief, which become rarer.
Despite the advent of many treatments, many OCD patients find little relief. Patients and practitioners are turning to Ketamine.
In this deep dive, we’ll unpack the science behind Ketamine, chart its integration into OCD treatment, and address the ethics of its use. We’ll also spotlight personal stories that show its positive impact.
Read on to learn more about ketamine for OCD.
Understanding Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
At the heart of OCD lies a complex interplay between thoughts, behaviors, and emotions. Sufferers often grapple with obsessions. These are persistent, unwanted thoughts or mental images that cause severe anxiety.
They also face compulsions. These are repetitive behaviors that one feels compelled to do. They often do them to relieve the anxiety.
This chronic condition affects people from all walks of life. It derails careers, relationships, and personal fulfillment. Traditional OCD ketamine treatments include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
They help many. Yet, many with OCD are treatment-resistant. This underscores the urgent need to explore other approaches.
The Ketamine Revolution
Ketamine was developed in the 1960s. Because of its dissociative properties, it was used for anesthesia. Its recent entry into mental health care began with a lucky observation.
In some patients, Ketamine infusions help with chronic pain or depression. They also had an unexpected but welcome impact on OCD symptoms.
The Ketamine treatment is like a medical odyssey. Patients are guided through a monitored process. It consists of a series of infusions held in a spa-like environment.
They emerge from the fog of the Ketamine state. Many report a big drop in their OCD symptoms.
The Science of Ketamine and OCD
What makes Ketamine a standout tool in the treatment of OCD? At a fundamental level, the answer lies in its mechanism of action.
SSRIs build up in the body to adjust serotonin levels. Unlike them, Ketamine works on a different system, the glutamatergic axis.
Glutamate is the brain’s primary excitatory neurotransmitter. It is linked to learning, memory, and, most, neuroplasticity. Ketamine blocks some glutamate receptors.
Ethical Considerations and the Future of Ketamine Treatment
The rise of Ketamine in mental health care has controversies and ethical dilemmas. Using Ketamine for psychiatric disorders off-label has prompted debates. They are about its safety, potential for abuse, and accessibility.
Concerns over Ketamine’s potential abuse are valid. This is especially true given its history as a recreational drug. Also, the rise of Ketamine clinics without strict medical oversight is about.
In the context of expanding treatment options for OCD and related anxiety disorders, the availability and approach toward anxiety therapy in Edmonton are noteworthy. Edmonton’s healthcare system has been adopting innovative treatments, including the use of Ketamine, to cater to individuals grappling with persistent anxiety disorders where traditional therapies have fallen short.
Understanding the Ketamine for OCD
In conclusion, the story of ketamine for OCD is one of fantastic change. What began as an incidental observation has burgeoned into a new frontier of hope for those who live under the shadow of this debilitating condition. With careful stewardship and a commitment to furthering scientific understanding, Ketamine stands poised as a revolutionary puzzle piece within the larger mosaic of mental health care.
For more helpful tips, check out the rest of our site today!
HEALTH
Helpful Tips for Those Suffering With Chronic Pain

Living with chronic pain can be a crippling and stressful experience that affects all facets of your life, including your mental and physical health. Regaining control over your pain is crucial, regardless of whether you have fibromyalgia, arthritis, chronic back pain, or any ailment that causes you discomfort.
Understanding Your Pain and Its Causes
Understanding your pain and its underlying causes is the first step toward properly treating chronic pain. Numerous things, such as trauma, inflammation, nerve damage, or underlying medical disorders, can cause chronic pain. Consider the location, degree, duration, and any triggers or mitigating variables for your pain as you take some time to evaluate your symptoms. To monitor your symptoms and spot any trends or triggers that could be aggravating your pain, keep a pain diary. Understanding the underlying causes of your pain will enable you to collaborate with medical specialists to create a customized treatment plan that takes into account your unique requirements and concerns.
Exploring Treatment Options and Therapies
Investigate different therapy and treatment options that can help reduce your symptoms and enhance your quality of life as soon as you have a better knowledge of your pain and its underlying causes. Treatment options can include prescription or over-the-counter drugs, physical therapy, chiropractic care, acupuncture, massage therapy, or nerve blocks, depending on the kind and intensity of your pain. Furthermore, by encouraging relaxation, lowering stress, and enhancing general well-being, complementary and alternative treatments, including yoga, tai chi, meditation, and mindfulness-based stress reduction approaches, can provide further relief from chronic pain.
Incorporating Lifestyle Modifications for Pain Management
Lifestyle changes can be quite helpful in controlling chronic pain and enhancing your general well-being, in addition to medical therapies and treatments. Make self-care routines that support both physical and mental well-being a priority, such as consistent exercise, a balanced diet, enough sleep, and stress reduction. Walking, swimming, or cycling are examples of low-impact workouts that can enhance cardiovascular health, flexibility, and strength without increasing the chance of injury or worsening discomfort. To promote optimum nutrition and lower inflammation, keep a well-balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats. Use stress-reduction methods to ease your mind and release tension, which can aggravate pain sensations. Some of these methods include progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing, and guided imagery.
Building a Support Network and Seeking Professional Help
It might be lonely to live with chronic pain, but you don’t have to go through this path by yourself. Creating a network of friends, family, and medical professionals who can relate to your experiences can be very helpful in terms of both practical support and emotional support. Seek support, empathy, and company from your loved ones, and don’t be afraid to ask for assistance when required with everyday duties or obligations. Consider joining online forums or support groups for people with chronic pain as well. These spaces allow you to interact with others who have experienced similar things, share resources and information, and provide encouragement and support to one another.
Going to a Clinic for Specialized Care
Consider obtaining specialist care at a pain management clinic if you’ve tried a variety of therapies and interventions but are still unable to find relief from chronic pain. Pain management clinics are specialized medical establishments manned by medical specialists with expertise in the diagnosis and treatment of persistent pain disorders, so it’s important to find a Chicago headache clinic or one in your area depending on what type of pain you are experiencing. These clinics provide thorough assessments, individualized treatment programs made to meet the specific requirements of each patient, and diagnostic testing. Medication management, interventional techniques, physical therapy, psychiatric counseling, and complementary and alternative treatments are a few possible treatment choices. Furthermore, access to multidisciplinary care teams—which include pain experts, physical therapists, psychiatrists, and nutritionists—who work together to address the intricate and multidimensional nature of chronic pain is often made possible by pain management clinics.
Conclusion
Although managing chronic pain can be difficult, it’s important to keep in mind that there are helpful treatment choices and tactics available to assist you in finding relief and enhancing your quality of life. You’re not alone. In your quest for pain treatment, keep in mind to be persistent and patient, and don’t be afraid to ask for assistance when you need it. You can experience relief from chronic pain and lead a more active, fulfilling life without having to worry about being in pain all the time with commitment and assistance.
HEALTH
From Headaches to Back Pain: The Versatile Benefits of Chiropractic Adjustments
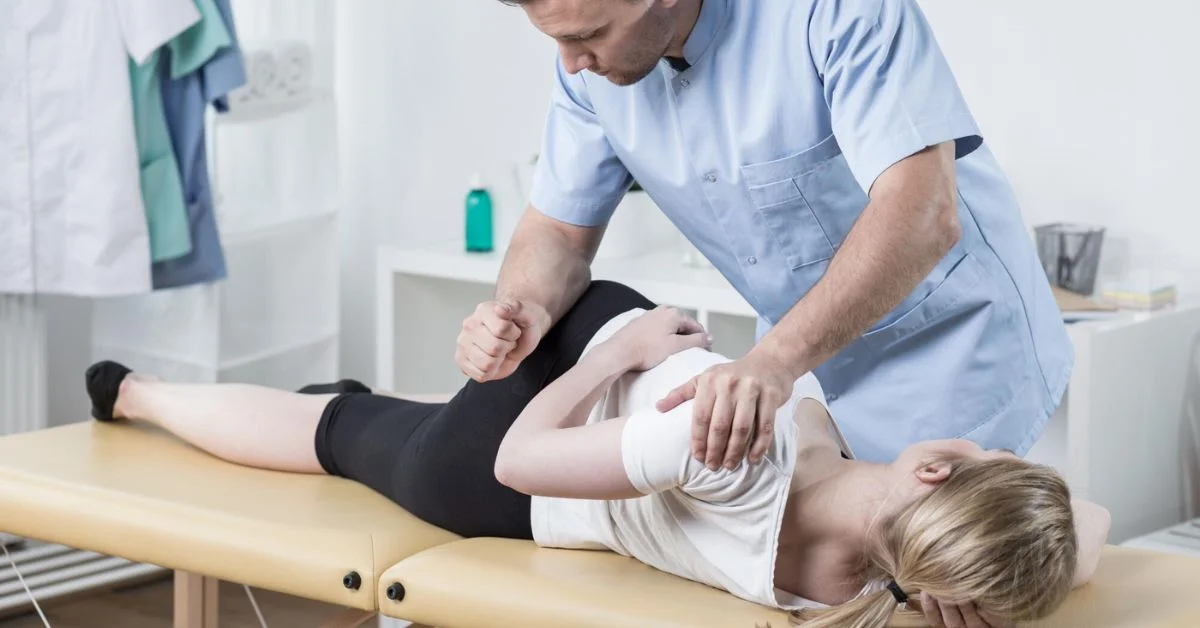
Did you know that about 22 million Americans visit chiropractors annually?
Chiropractic care has become popular over the years. This is due to its effectiveness in treating a wide range of health issues. This includes headaches, neck pain, back pain, and joint problems.
It involves making adjustments to the spine to improve health and alleviate pain. But the benefits of chiropractic adjustments go far beyond just pain relief.
In this article, we will explore the versatile benefits of chiropractic care. Read on to learn more.
Improved Nervous System Function
The nervous system is responsible for controlling every cell and organ in our body. Misalignments in the spine can disrupt the communication between the brain and the body. This leads to a variety of health issues.
Chiropractic adjustments help to realign the spine. This improves the nervous system function and promotes overall wellness. It can also strengthen the body’s ability to fight off illness and disease.
Better Posture
Poor posture can cause a lot of strain on the spine. This leads to back pain and other health problems.
Chiropractic adjustments correct misalignments in the spine, resulting in better posture. This can also prevent future injuries and improve athletic performance.
Increased Range of Motion
Restricted movement and stiffness are common symptoms of joint issues. This can limit our ability to perform daily tasks and activities.
Chiropractors can help to increase the range of motion in joints. They use gentle techniques to mobilize the joints and reduce pain. This results in improved flexibility and mobility.
Headache Relief
Headaches are a common health issue that can be caused by tension in the neck and back. Chiropractic adjustments can help to relieve this tension, providing relief from headaches. It also helps to address the root cause of the pain rather than just masking it with medication.
Neck pain can also contribute to tension headaches. Chiropractic help for neck pain can provide relief and help to prevent future occurrences of headaches.
Improved Sleep
Many people struggle with sleep issues such as insomnia or poor sleep quality. Chiropractic methods can help to improve sleep by reducing pain and tension in the body. It can also promote relaxation and reduce stress levels, resulting in better sleep.
Reduction in Osteoarthritis Symptoms
Chiropractic care is beneficial in managing symptoms of osteoarthritis. By maintaining proper alignment and mobility, chiropractic adjustments can decrease the wear and tear on joints. This can reduce pain and stiffness associated with osteoarthritis.
It can also slow down the progression of the disease. This makes chiropractic care a valuable addition to the treatment plan for those suffering from osteoarthritis.
Relief from Pregnancy-Related Discomfort
Many pregnant women experience back pain, neck pain, and joint discomfort due to the physical changes that occur during pregnancy. Chiropractic care is a safe and effective way to relieve these discomforts.
Adjustments can help to balance the pelvis, reduce spinal nerve stress, and enhance overall comfort. It can also help to position the baby properly for birth.
Exploring the Benefits of Chiropractic Adjustments
The benefits of chiropractic adjustments go beyond just treating pain and discomfort. It can improve overall health and wellness by addressing the root cause of health issues.
With its versatility, chiropractic adjustments can benefit people of all ages and backgrounds. Consider scheduling a chiropractor appointment to experience these versatile benefits for yourself. Your body will thank you for it!
Did you find this blog post helpful? If so, feel free to explore more of our blog!
FOOD & DRINKS
Nutrition and Erectile Health: Superfoods for Better Performance
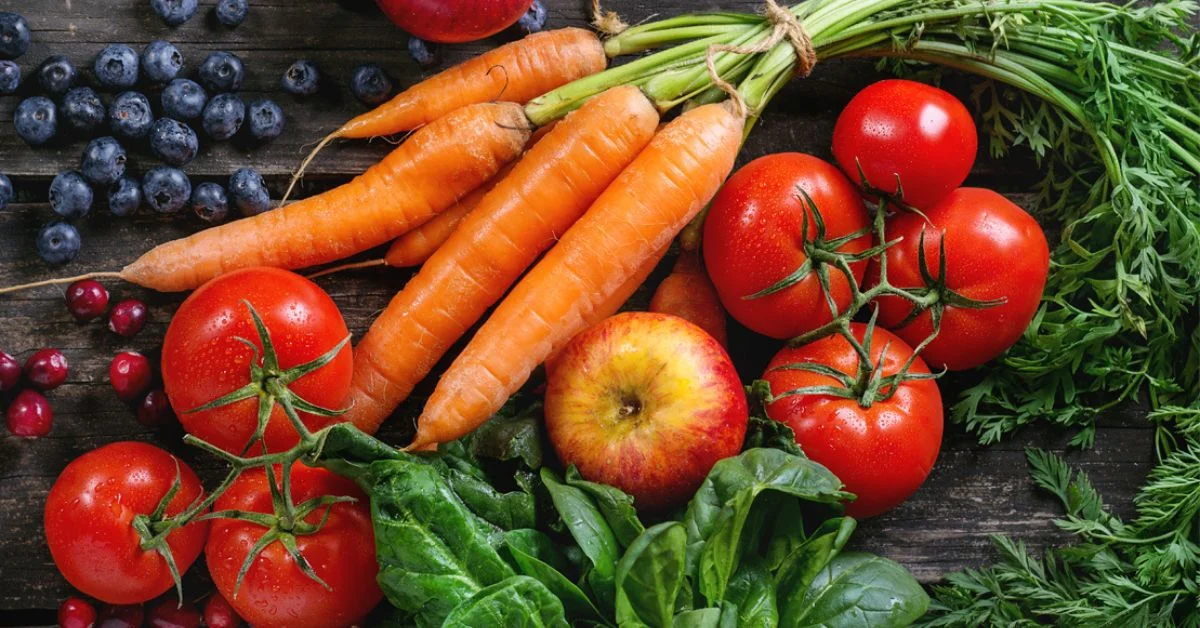

In the quest for overall health and vitality, nutrition plays a pivotal role. While many discussions focus on physical fitness and disease prevention, the impact of nutrition on specific aspects of health, such as erectile health, is often overlooked. By incorporating superfoods into your diet, you can nourish your body and support better performance in various aspects of life, including those moments of intimacy.
Introduction
Nutrition is the foundation of good health, influencing everything from energy levels to immune function. When it comes to erectile health, the foods you eat can have a significant impact on blood flow, hormone balance, and overall cardiovascular health. In this article, we’ll explore some superfoods that can support better performance in various aspects of life, including moments of intimacy.
The Power of Superfoods
Superfoods are nutrient-dense foods that offer a wide range of health benefits. From boosting immunity to supporting heart health, these foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytochemicals that nourish the body and promote overall well-being.
While medications like Cenforce 150 and Fildena 150 can offer temporary relief for performance issues, true vitality comes from within. By prioritizing nutrition and incorporating superfoods into your diet, you can support overall health and well-being, including erectile health. So, next time you’re looking to enhance your performance, consider reaching for a plate of nutrient-packed superfoods. Your body will thank you for it.
Superfoods for Erectile Health
- Dark Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are rich in nitrates, compounds that help improve blood flow by dilating blood vessels. This enhanced circulation can benefit erectile function by promoting healthy blood flow to the genitals.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are loaded with antioxidants, which help protect blood vessels from damage caused by oxidative stress. By reducing inflammation and supporting vascular health, berries can contribute to better erectile function.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and pumpkin seeds are excellent sources of arginine, an amino acid that plays a role in the production of nitric oxide. Nitric oxide helps relax blood vessels, allowing for increased blood flow to the genitals and improved erectile function.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and trout are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and support cardiovascular health. By reducing inflammation and improving blood flow, omega-3 fatty acids may help enhance erectile function.
Incorporating Superfoods Into Your Diet
Adding superfoods to your diet doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some simple ways to incorporate these nutrient-packed foods into your daily meals:
- Smoothies: Blend leafy greens, berries, nuts, and seeds into a delicious smoothie for a nutrient-packed breakfast or snack.
- Salads: Add dark leafy greens, berries, and nuts to your salads for a burst of flavor and nutrition.
- Trail Mix: Create your own trail mix with nuts, seeds, and dried berries for a satisfying and nutritious snack.
- Grilled Fish: Enjoy fatty fish like salmon or trout grilled with a side of leafy greens for a heart-healthy meal.
Conclusion
This article highlights the importance of nutrition in supporting erectile health and suggests incorporating superfoods into the diet as a natural approach to promoting better performance. Additionally, it mentions medications like Cenforce 200 and Fildena as part of a broader discussion on wellness.

 BUSINESS1 year ago
BUSINESS1 year agoExploring the Benefits of Commercial Printing

 HOME IMPROVEMENT12 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT12 months agoThe Do’s and Don’ts of Renting Rubbish Bins for Your Next Renovation

 BUSINESS12 months ago
BUSINESS12 months agoBrand Visibility with Imprint Now and Custom Poly Mailers

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoThe Surprising Benefits of Weight Loss Peptides You Need to Know

 TECHNOLOGY10 months ago
TECHNOLOGY10 months agoDizipal 608: The Tech Revolution Redefined

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoYour Guide to Shedding Pounds in the Digital Age

 HOME IMPROVEMENT8 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT8 months agoGet Your Grout to Gleam With These Easy-To-Follow Tips

 HEALTH11 months ago
HEALTH11 months agoHappy Hippo Kratom Reviews: Read Before You Buy!












