TECHNOLOGY
What Is Audio Bitrate and Why Does It Matter?
Audio bitrate is a crucial factor in determining the quality and size of audio files. It represents the amount of data processed per second when playing an audio file, typically measured in kilobits per second (kbps). The bitrate directly influences how sound is experienced, whether listening to music, watching a video, or engaging in a conference call. Understanding audio bitrate helps ensure the best sound quality for your specific needs, balancing quality and file size for various applications. This guide explores audio bitrate‘s key concepts, impacts on sound quality, and tips for choosing the right bitrate.
What Is Audio Bitrate?
Defining Audio Bitrate
Audio bitrate refers to the number of bits processed per second in an audio file, denoting how much data is used to encode the audio signal. Higher bitrates mean more data is used, resulting in better sound quality but larger file sizes. The bitrate is essential in audio compression, influencing the clarity and richness of sound. Common bitrates for music files range from 128 kbps to 320 kbps, while high-resolution audio can reach up to 1411 kbps or more.
Bitrate and Audio Quality
Audio quality is significantly affected by bitrate, with higher bitrates generally offering superior sound. A higher bitrate allows more detailed audio data, producing clearer and more nuanced sound. For example, 128 kbps is often used for standard MP3 files, providing decent quality for casual listening. However, for those seeking a richer audio experience, bitrates of 256 kbps or 320 kbps are preferred. High-resolution audio files, such as FLAC or WAV, utilize even higher bitrates, preserving more of the original sound nuances and delivering a listening experience closer to the source.
How Does Audio Bitrate Affect Sound Quality?
Comparing Common Bitrates
When comparing audio bitrates, noticeable differences emerge in sound quality. A file with a bitrate of 128 kbps may sound satisfactory for everyday listening, especially on portable devices or through streaming. However, at 256 kbps or 320 kbps, the sound becomes noticeably more dynamic and full, with enhanced clarity and depth. These higher bitrates are ideal for music enthusiasts who want to capture the intricacies of musical performances. Additionally, high-resolution formats use bitrates exceeding 1000 kbps, delivering unparalleled sound quality that replicates the original recording with minimal loss.
Impact on Different Formats
Different audio formats utilize bitrates differently, affecting quality and file size. MP3 is a popular format that compresses audio to save space, often at 128 kbps or 256 kbps. In contrast, AAC and OGG formats offer improved compression efficiency, providing better sound quality at similar bitrates. Lossless formats like FLAC and ALAC retain all audio information, allowing for bitrates of up to 1411 kbps or more. These formats deliver superior audio fidelity, making them the choice for audiophiles who prioritize quality over file size.

Variable vs. Constant Bitrate: Which Is Better?
Understanding Variable Bitrate (VBR)
Variable Bitrate (VBR) dynamically adjusts the bitrate throughout the audio file based on its complexity. This method allocates higher bitrates to complex sections while using lower bitrates for simpler parts, optimizing sound quality and file size. VBR provides better overall sound quality than Constant Bitrate (CBR) at equivalent average bitrates, as it preserves more detail in complex audio sections. VBR is ideal for music files where varying sound complexity is present, allowing for efficient storage without sacrificing quality.
Exploring Constant Bitrate (CBR)
Constant Bitrate (CBR) maintains a fixed bitrate throughout the audio file, ensuring consistent data use across all sections. This approach is straightforward and ensures predictable file sizes, making it suitable for streaming where consistent bandwidth usage is essential. CBR is easier to process and compatible with various devices and software. Although it may not optimize sound quality like VBR, CBR remains a reliable choice for applications where consistent performance and compatibility are crucial.
Choosing the Right Bitrate for Your Needs
Streaming vs. Downloading
Streaming and downloading audio require different bitrate considerations. Streaming demands efficient use of bandwidth, making lower bitrates like 128 kbps or 192 kbps more suitable to ensure smooth playback and minimal buffering. Tencent RTC, a leading provider of real-time communication services, optimizes streaming experiences by adjusting bitrates dynamically based on network conditions. In contrast, downloading audio allows for higher bitrates, such as 256 kbps or 320 kbps, to maximize sound quality, especially when storage space is not a limiting factor.
Device and Environment Considerations
The choice of bitrate should consider the device and listening environment. High-quality headphones or speakers can reveal the nuances of higher bitrates, making them ideal for dedicated listening sessions at home. In contrast, lower bitrates may suffice for portable devices or noisy environments where sound quality is less discernible. Consideration of storage capacity, battery life, and data usage is also essential when selecting the appropriate bitrate, ensuring a balance between quality, file size, and practicality.
Conclusion
Understanding audio bitrate is key to optimizing sound quality and file size for various applications. Higher bitrates generally provide better sound but result in larger files, necessitating a balance based on specific needs. By considering factors like audio format, listening environment, and intended use, you can select the right bitrate for your situation. Whether prioritizing quality with high-resolution formats or efficiency with lower bitrates, an informed choice ensures the best audio experience, tailored to your preferences and requirements.
GADGETS
WiFi Affiliation Block: Causes and Blueprints

WiFi network plug up happens when different gadgets seek data move limit on a far off affiliation, instigating slow rates, dropped affiliations, and debilitated clients. As how much contraptions related with WiFi networks keeps on making, blockage has changed into a typical issue for both home and experience affiliations. In this article, we will look at the clarifications behind WiFi network plug up and give manages assist with alleviating this issue.
Purposes behind WiFi Affiliation Plug up:
1. *Increased Number of Devices*: The more contraptions related with your WiFi affiliation, the more data transmission should help them. This can incite blockage, particularly on the off chance that your affiliation isn’t prepared to deal with the drawn out interest.
2. *Bandwidth-Concentrated Applications*: Applications like electronic features, web gaming, and report sharing require a great deal of move speed, which can cause blockage on your affiliation.
3. *Physical Obstructions*: Certifiable counteractions like walls, floors, and housetops can weaken your WiFi https://100001pisowifi.uno/ signal, actuating blockage and dropped affiliations.
4. *Interference from Lining Networks*: On the off chance that you live in a thickly populated locale or have neighbors with WiFi affiliations, their signs can disturb yours, causing blockage.
5. *Outdated Switch Firmware*: Tolerating your switch’s firmware is old, it can no question not deal with the requesting of your affiliation, impelling blockage.
Manages any outcomes with respect to WiFi Affiliation Blockage:
1. *Upgrade Your Router*: Consider moving to a fresher, significantly more vital switch that can deal with the sales of your affiliation.
2. *Use Nature of Association (QoS) Settings*: QoS settings award you to focus in on unambiguous contraptions or applications on your affiliation, guaranteeing that fundamental traffic gets the data move restrict it needs.
3. *Implement a Visitor Network*: Setting up an other visitor affiliation can assist with lessening blockage by restricting how much contraptions searching for data transmission on your significant affiliation.
4. *Use a WiFi Analyzer App*: WiFi analyzer applications can assist you with seeing channels with less impedance, permitting you to change to a less discouraged channel.
5. *Implement an Affiliation Access Control (NAC) System*: NAC structures permit you to control who advances toward your affiliation, diminishing the bet of unapproved gadgets interfacing and causing blockage.
6. *Use a Cross fragment Affiliation System*: Lattice network structures utilize different ways of giving huge strong regions for a, connection all through your home or office, reducing hinder and dropped affiliations.
7. *Limit Data transmission Serious Applications*: Consider restricting the utilization of move speed raised applications during top use times to reduce plug up.
8. *Use a WiFi Show up at Extender*: WiFi https://1001pisowifi.com range extenders can assist with enlarging your affiliation’s fuse region, decreasing blockage and dropped affiliations.
9. *Update Your Switch’s Firmware*: Consistently update your change’s firmware to guarantee you have the most recent elements and execution overhauls.
10. *Conduct an Affiliation Audit*: Planning an affiliation overview can assist you with seeing areas of blockage and give thoughts to progress.
In light of everything, WiFi network block is an ordinary issue that can be accomplished by various parts. By figuring out the reasons behind blockage and doing the plans illustrated above, you can assist with diminishing this issue and give a speedier, more reliable WiFi experience for your clients.
TECHNOLOGY
From Start to Finish: How a Solar Consultation Sets You Up for Success
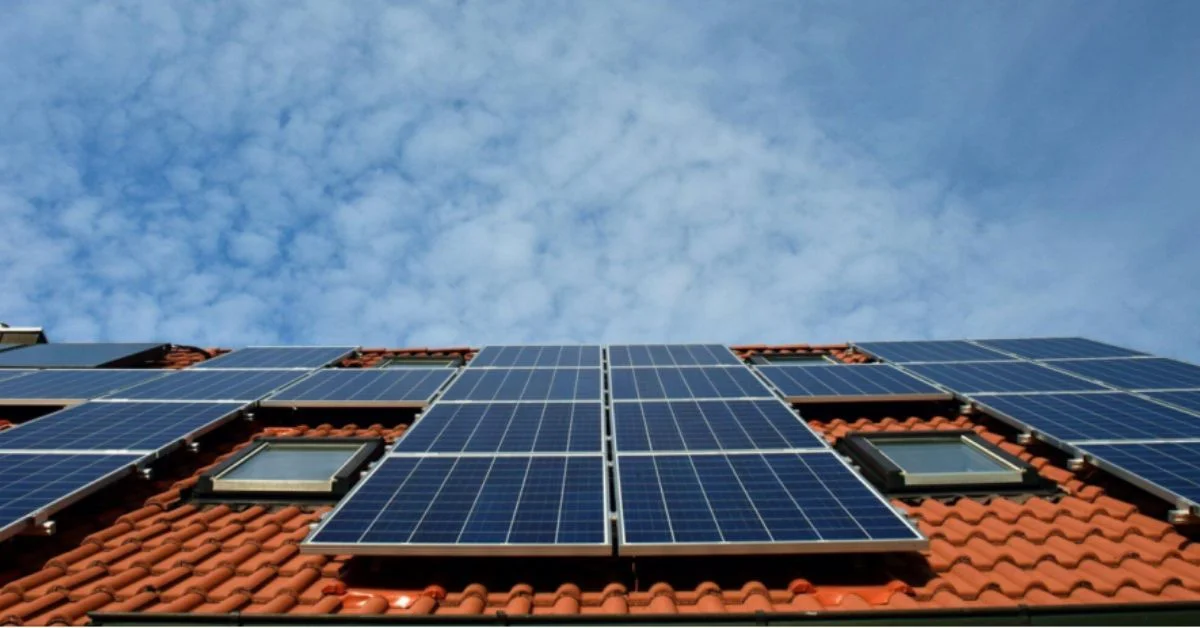

Considering the shift towards solar energy can be a big move for any homeowner. It’s not just about the installation, it’s about understanding how solar power fits into your daily life and its benefits. That’s where solar consultation comes in handy.
This important step helps you make an informed decision by evaluating your home’s suitability for solar panels, the potential savings on energy costs, and the environmental benefits. In this blog, we will discuss how a solar consultation sets you up for success.
Understanding Your Needs
During a solar consultation, a solar consultant does a deep dive into how you use energy in your home. They look at your past electricity bills to see when you use the most power and how much you pay. This will help them figure out the best solar setup for your house.
Knowing this, the solar expert can tell you how many panels you’ll need to cover your energy use. They consider the direction your roof faces and if shadows from trees or buildings might block the sun. With this info, they help you see how solar power can lower your bills and help the planet.
Site Assessment
Site assessment is a key step in moving forward with solar energy. This is when a solar energy contractor comes to your home to take a close look at your roof. They check if it’s in good shape and gets enough sunlight for solar panels.
The contractor measures your roof and checks for any issues that might make installing panels hard. They also look at trees or buildings that could block sunlight from reaching your roof. This helps them plan where to put the panels for the best sun exposure.
Customized Solutions
After understanding your home’s unique needs and completing a site assessment, solar developers create a personalized plan for your solar installation. They choose the right type and number of panels that fit best on your roof and match your energy needs. This means you get a system that’s just right for you, not too big or too small.
Their plan also looks at how to save you the most money on your energy bills and make sure your home makes the most of the sun’s power. They will work with you to find the best way to set everything up. This way, you can be sure your move to solar energy is smart and smooth.
Financial Analysis
A big part of deciding to go solar is looking at the money side of things. In the financial analysis part of your solar consultation, experts will tell you how much the whole solar system will cost and how you can save money in the long run. They check things like tax breaks and special solar programs in your area to make it cheaper for you.
They also figure out how long it will take for the savings on your energy bills to pay back the cost of the solar panels. This is called the payback period. Knowing this helps you see how good of an investment solar energy is for your home and future.
Product and Technology Guidance
Choosing the right solar technology and products is a big part of making your solar energy system work its best. During the consultation, experts explain the differences between types of solar panels and batteries. They help you pick the ones that fit your energy needs and budget.
The latest in solar panel technology can make a big difference in how much power you get. For a reliable solar panel installation, consider the services provided by companies such as Edmonton Solar Power. Your solar consultant will tell you about the newest and most efficient options. They make sure you have all the information to choose the best technology for your home.
Permitting and Regulations
Navigating the world of permits and regulations is a vital step in the solar installation process. Your solar consultant will guide you through getting the necessary permits and making sure your solar system meets local building codes. This ensures everything is done right and legally, avoiding future problems.
Understanding the rules about solar panels in your area helps make the installation go smoothly. The consultant will check these rules and talk to the local authorities for you. This way, you won’t face unexpected issues or delays in getting your solar system up and running.
Installation Planning
When it’s time to set up your solar panels, planning is essential. Your solar team will pick a day that works best for you to start the work. They make sure everything needed is ready before they begin.
The installation usually takes a few days, depending on your home’s size and the system. Solar experts handle all the heavy lifting, from setting up the panels to making sure they’re properly connected. They do everything safely and check to see if the system works right.
Quality Installation
Quality installation means making sure your solar panels work great from the start. Expert solar installers in Charleston focus on doing the job right the first time. They use top tools and follow strict rules to set up your solar system.
These experts check every part of the installation carefully. They want to make sure your panels catch as much sun as possible. After they finish, they test everything to ensure your system is ready to go.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Monitoring and maintenance are key to keeping your solar panels working well. Your solar company will show you how to keep an eye on your panel’s performance, often through a simple app on your phone. If there’s a problem, they’ll spot it fast and get it fixed.
Regular check-ups can help your solar panels last longer and provide more power over time. The solar team checks for dirt, leaves, or anything else that could block sunlight.
Brightening Your Tomorrow with a Solar Consultation
Choosing to explore solar energy with a solar consultation is a smart move. It guides you through every step, making sure solar fit your home just right. From the very start, experts help you understand how solar can benefit you, making it easy and clear.
Solar consultation opens the door to saving on bills and using clean energy. The specialists work out all the details, so you don’t have to worry. In the end, your home becomes more eco-friendly, and you know exactly how solar improves your life.
If you find this article helpful, you may visit our blog for more content.
TECHNOLOGY
Which Industries Benefits Gain From Rapid Prototypes of Sheet Metal?
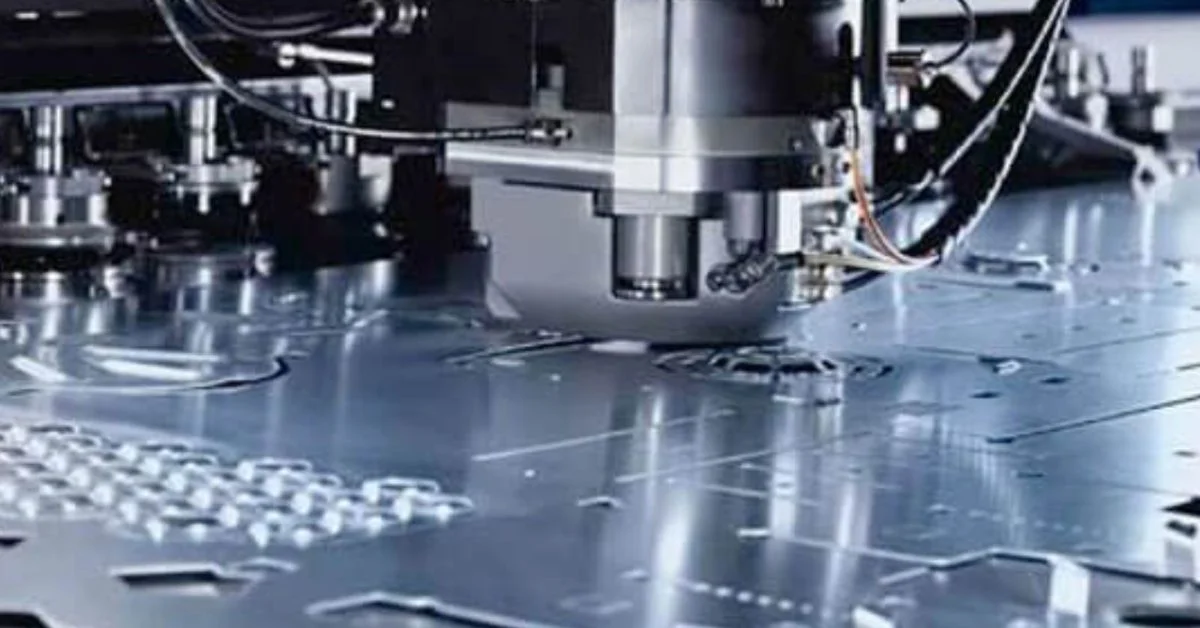

Rapid sheet metal prototyping services contain the short and efficient advent of metallic elements for prototypes and preliminary product designs. These offerings are utilized in industries like car, aerospace, consumer electronics, and machinery to produce custom steel components for checking out and assessment.
Using the use of advanced production strategies which include laser slicing, CNC bending, and punching, fast sheet steel prototyping allows engineers and designers to evaluate the shape, suit, and characteristics of steel parts in a brief time frame. The method starts with a CAD layout, which is converted into metal elements with the usage of a precision fabrication device.
Materials like aluminum, steel, and stainless steel are widely employed in speedy prototyping due to their versatility and durability. This method permits corporations to iterate designs, become aware of issues early, and make important modifications before mass manufacturing. Rapid Sheet Metal Prototyping services offer a price-effective and time-saving solution for developing superb, customized metal components.
What’s The Position of Sheet Metal Prototyping in Manufacturing?
Sheet steel prototyping plays an essential position in production by enabling the introduction of preliminary designs and fashions of metal products for trying out and assessment earlier than complete-scale manufacturing. This method allows producers to speedy iterate and refine designs primarily based on comments and overall performance tests, assisting in perceiving and rectifying potential problems early in the development cycle.
Sheet metal prototyping is vital for making sure that a layout meets the favored specifications, functional necessities, and great standards. It affords a cost-effective manner to discover specific materials, fabrication techniques, and design options, that may in the end improve product performance and performance.
Additionally, prototyping allows manufacturers to optimize manufacturing procedures, lessen lead times, and limit waste. Via permitting the creation of accurate and reliable prototypes, sheet metallic prototyping helps innovation and allows producers to deliver merchandise to market faster and more efficiently.
Industrial Benefits Of Rapid Sheet Metal Prototyping
Rapid sheet metal prototyping is a treasured manufacturing method that advantages a wide range of industries. This method permits for the short fabrication of metal elements through the usage of diverse techniques which include laser slicing, bending, and stamping. It’s far known for its velocity, value-effectiveness, and potential to supply exquisite merchandise. Right here are some industries that gain from fast sheet metallic prototyping:
- Aerospace and Protection
The aerospace and defense industries benefit drastically from fast sheet metal prototyping because of its capability to produce particular, superb additives quickly. This manner supports the advent of complicated parts with tight tolerances required for aircraft and protection systems. It hastens the development of the latest designs and systems whilst ensuring they meet strict protection and performance standards, leading to faster innovation and time-to-marketplace for aerospace and protection products.
- Automobile
The automotive enterprise blessings from rapid sheet metallic prototyping by way of permitting quick manufacturing and checking out of car components and designs. This manner is especially beneficial for creating prototypes of body panels, chassis, and structural parts. It hurries up improvement cycles, permitting automakers to optimize and refine designs unexpectedly. Using reducing time-to-marketplace, car manufacturers can carry new fashions and innovations to consumers more effectively and live aggressively within the industry.
- Consumer Electronics
In the client electronics industry, rapid sheet metal prototyping is instrumental in generating enclosures, instances, and structural components for gadgets. This process permits manufacturers to speedy check and refine designs, ensuring merchandise is both useful and aesthetically appealing. The rate of prototyping allows corporations to deliver modern merchandise to the marketplace quicker and adapt to converting traits. Additionally, it helps the production of durable, unique, and price-powerful additives that decorate the overall exceptional and reliability of electronic gadgets.
- Scientific Devices
Fast sheet metal prototyping performs a critical function within the medical device industry by facilitating the fast and precise fabrication of medical equipment and gadgets. This manner allows producers to create prototypes for gadgets such as surgical tools, diagnostic equipment, and monitoring devices with high accuracy and reliability. It supports rapid testing and adjustments to designs, ensuring that scientific devices meet stringent safety and regulatory requirements. As a result, improvements may be introduced to the market correctly, improving patient care.
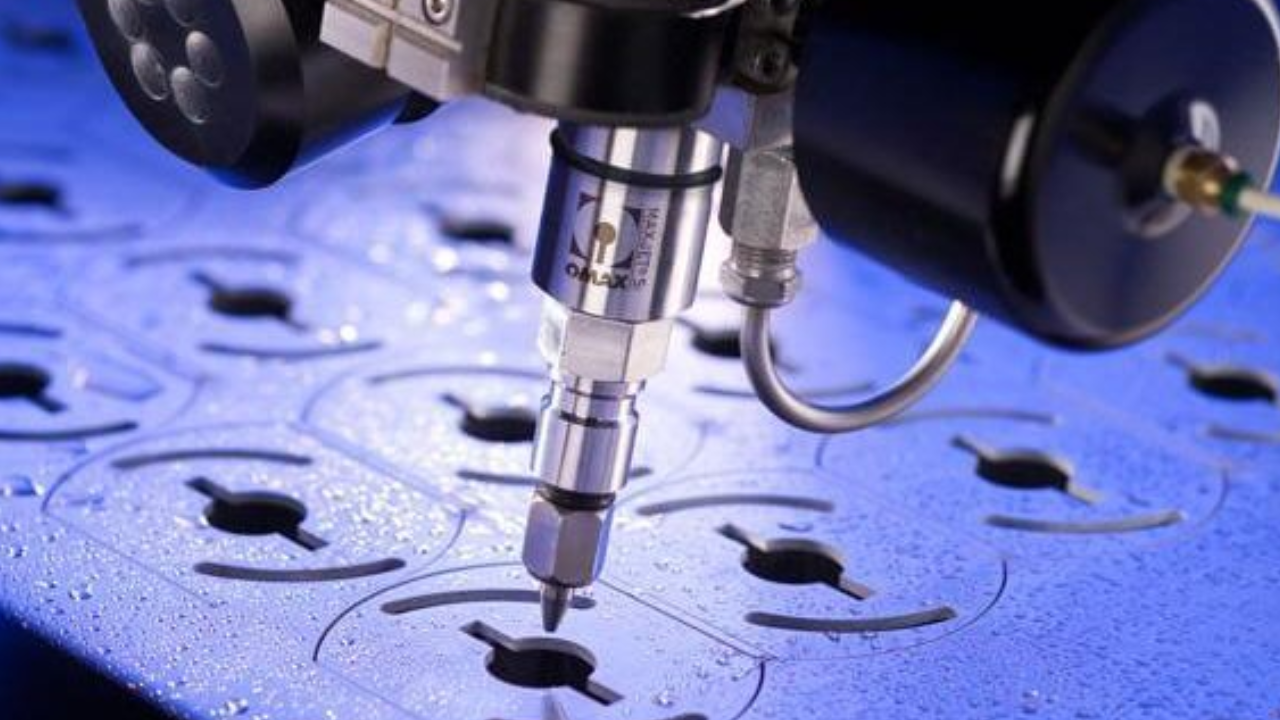

- Telecommunications
Inside the telecommunications industry, speedy sheet metal prototyping is important for producing enclosures and mounting brackets for community systems inclusive of antennas, routers, and base stations. This manner permits producers to unexpectedly increase and check new designs, ensuring components are durable, precise, and green. The fast turnaround helps the quick-paced nature of the industry, allowing for brief adjustments to designs based totally on evolving generation and market demands. This agility allows preserve strong and reliable verbal exchange networks.
- Energy and Utilities
The energy and utility industries advantage of speedy sheet steel prototyping by way of allowing the fast and particular fabrication of components and components for strength era, transmission, and distribution. This includes enclosures for electric systems, helps for sun panels, and components for wind turbines. The system lets in for fast trying out and optimization of recent designs, ensuring green and powerful strength solutions. It supports the enterprise’s agility and responsiveness to changing power demands and advancements in renewable electricity technology.
- Industrial Machinery
Rapid sheet steel prototyping plays a key function in the business machinery enterprise by taking into account the quick fabrication of custom parts and additives for gadgets which include conveyors, presses, and assembly traces. The method permits fast trying out and optimization of the latest equipment designs, making sure of efficient manufacturing procedures. Manufacturers can hastily iterate and refine designs, reducing time-to-market for brand-new devices. This flexibility and performance help commercial machinery groups live competitively and meet the evolving desires of their clients.
- Structure And Production
Inside the structure and production industries, rapid sheet steel prototyping is invaluable for growing difficult designs and custom additives including facades, ornamental factors, and structural supports. This method permits architects and developers to speedy prototype and check progressive designs, making sure they are precise and pleasant. It also supports using modern-day materials and complex geometries in building tasks. By way of streamlining the design and fabrication procedure, fast sheet metallic prototyping facilitates carrying precise and innovative architectural visions to existence correctly.
Final Lines
Rapid sheet steel prototyping has revolutionized numerous industries with the aid of presenting pace, precision, and price effectiveness in fabricating high-quality metal components. From aerospace and car to consumer electronics and clinical devices, this system accelerates innovation and time-to-marketplace. It empowers industries to stay competitive, adapt to changing needs, and bring superior products and technology to the marketplace efficiently, paving the manner for endured growth and success across diverse sectors.

 BUSINESS1 year ago
BUSINESS1 year agoExploring the Benefits of Commercial Printing

 HOME IMPROVEMENT12 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT12 months agoThe Do’s and Don’ts of Renting Rubbish Bins for Your Next Renovation

 BUSINESS12 months ago
BUSINESS12 months agoBrand Visibility with Imprint Now and Custom Poly Mailers

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoThe Surprising Benefits of Weight Loss Peptides You Need to Know

 TECHNOLOGY10 months ago
TECHNOLOGY10 months agoDizipal 608: The Tech Revolution Redefined

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoYour Guide to Shedding Pounds in the Digital Age

 HOME IMPROVEMENT8 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT8 months agoGet Your Grout to Gleam With These Easy-To-Follow Tips

 HEALTH11 months ago
HEALTH11 months agoHappy Hippo Kratom Reviews: Read Before You Buy!












